Linting Tools
At mParticle, we have developed tools to allow you to statically lint code against your data plan as you develop. This allows you to adhere to your company’s data plan and ensures that high quality data is logged to your workspace. Click here to learn more about Data Plans and Data Master.
Setup
For all linters, you will need to download your data plan and have a file named mp.config.json (mParticle config file) at the root of your project. Inside of mp.config.json, reference your data plan’s file location. You can learn more about the mParticle config file here. The required key for your mParticle config file is planningConfig.
iOS
Our iOS linter lints Swift code. An example is below:
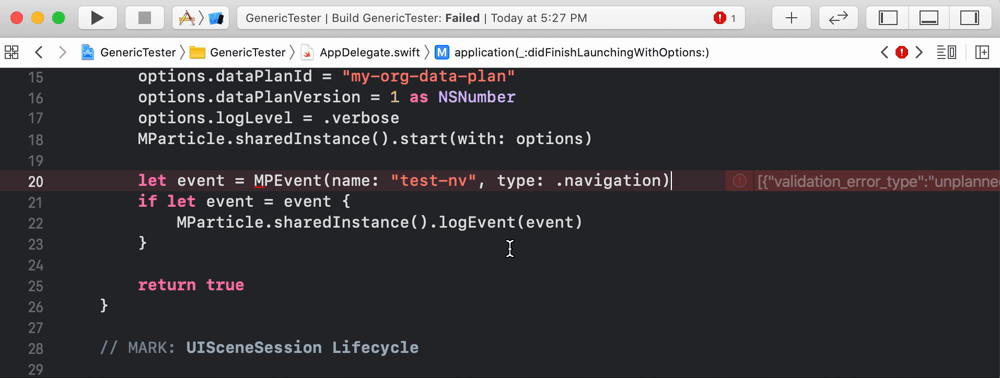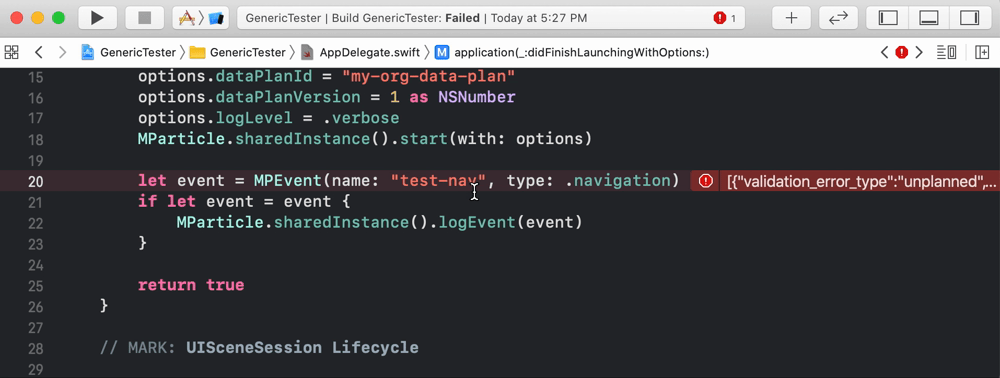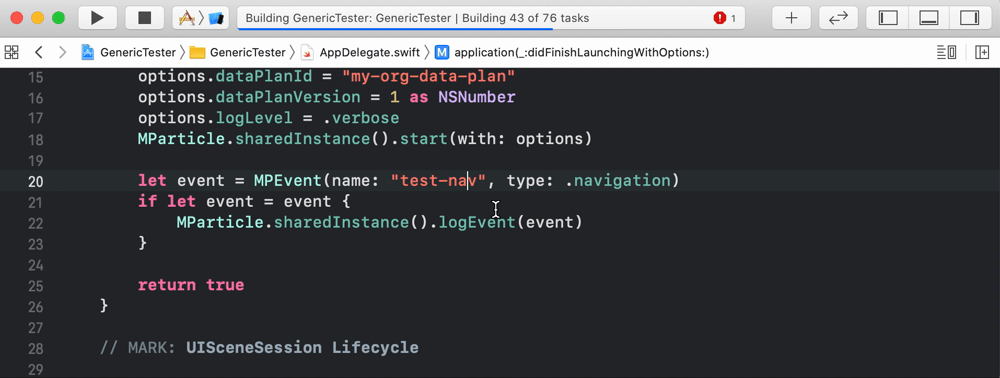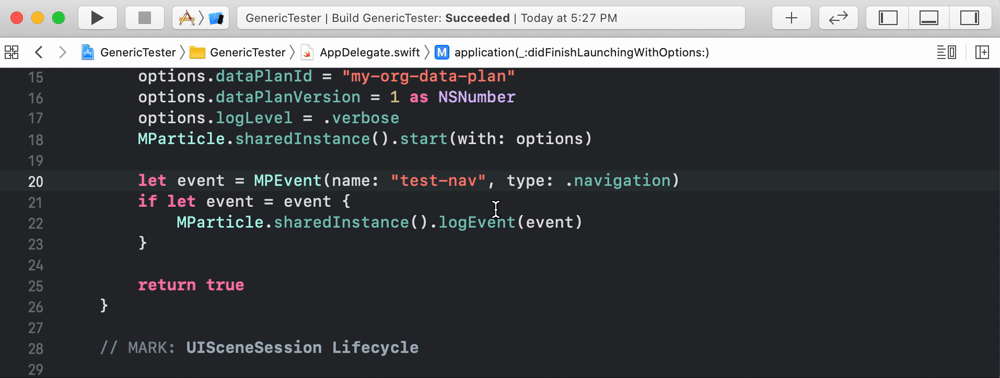
1. Setup prerequisites
Swift Linter requires macOS Catalina (10.15), npm, node, and the mParticle Command Line Interface
Note: Currently, linting requires that you to use version 1.0.3 of the mParticle CLI. If you have a later version, please uninstall the cli and reinstall version 1.0.3.
sudo npm install -g @mparticle/cli@1.0.32. Install the linter
Download and install the latest Swift Linter pkg file from the repository’s releases page.
3. Specify your Data Plan
Download your data plan from the mParticle platform and save it to a file in your source repository.
- Create a file
mp.config.jsonin your repository root to tell the linter where to find the data plan file. - The example below assumes you saved the downloaded file as
plan.jsonin the root of your repository. If you used a different path or filename, adjust thedataPlanVersionfield accordingly. - We also strongly recommend that you include the
lintingConfigsection below (customizing the values of theincludedandexcludedkeys as appropriate for your project), in order to limit the number of files that get processed by the linter to those that contain your mParticle implementation, otherwise it can hang due to trying to parse a large number of swift source files.
{
"planningConfig": {
"dataPlanVersionFile": "./plan.json"
},
"lintingConfig": {
"included": [
"MyViewController"
],
"excluded": [
"ContentView.swift"
]
}
}4. Configure your Xcode project and SDK options
To allow linting to take place automatically each time you build, add a new Run Script Build Phase to your project.
In the source editor for the new phase, simply invoke the Swift linter binary: /usr/local/bin/mpswiftlint
Optionally, you may want to reorder the build step near the top and/or rename the build step to something that will be easier to spot in build logs (e.g. mParticle Linter).
Finally, if you have not already done so, you should specify your dataPlanId and dataPlanVersion in MParticleOptions at the time of SDK initialization:
let options = MParticleOptions(key: "REPLACE WITH APP KEY", secret:@"REPLACE WITH APP SECRET")
options.dataPlanId = "my-org-data-plan"
options.dataPlanVersion = 1 as NSNumber
MParticle.sharedInstance().start(with: options))Using the linter
You are now ready to begin linting your code—simply build your project using Xcode and if the linter detects that your implementation doesn’t match the data plan, messages will appear inline and in Xcode’s issue navigator.
Data point implementation status
- Event names
- Event types
- Event attributes
Android
The Android SDK provides the ability to enforce your Data Plan via linting. It only runs in the build environment, so there is no chance that it affects the runtime behavior of the mParticle SDK.
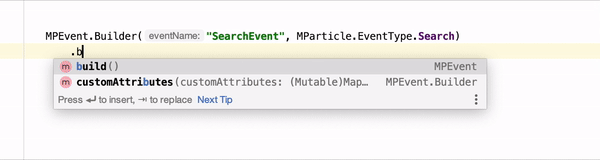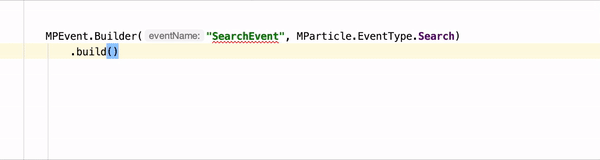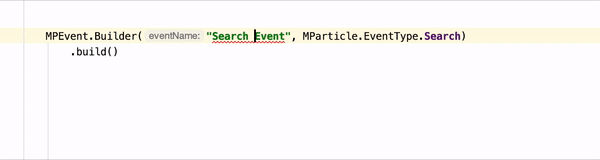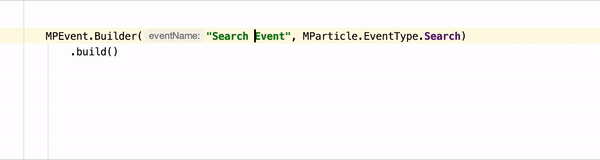
Android Linter requires npm, node, and the mParticle Command Line Interface
1. Add the mParticle Gradle Plugin
The next step is to configure the mParticle Gradle Plugin. In your root build.gradle use the following code to add the plugin dependency to your buildscript:
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
...
classpath 'com.mparticle:android-plugin:5.18.1' // See our latest version on [Maven](https://search.maven.org/artifact/com.mparticle/android-plugin)
}
}Next, apply the plugin in your project-level build.gradle
apply plugin: 'com.mparticle'2) Configure the Plugin
Either configure the mParticle Plugin object
mparticle {
dataPlanVersionFile 'mp-dataplan.json' //(required) filename or path
resultsFile 'mp-dp-results.json' //(optional) filename or path
disabled false //(optional) defaults to "false"
verbose false //{optional) defaults to "false"
}Or
provide an mp.config.json config file in the project-level directory
{
"dataPlanVersionFile": "mp-dataplan.json", //(required) filename or path
"resultsFile": "mp-dp-results.json", //(optional) filename or path
"disabled": "false", //(optional) defaults to "false"
"verbose": false //(optional) defaults to "false"
}3) Install the mParticle CLI tool
Install the mParticle CLI.
./gradlew mpInstall4) Viewing results
Note: Any changes to your dataplan are not applied until the Gradle Project Syncs
Validation Errors surface in multiple locations.
- Individual Errors in the IDE as linting errors (red squiggly underlines), marking the offending code.
- Written to your
resultsFile, if you configured one in the mParticle plugin - Within the terminal, run
./gradlew lint
Custom Lint Checks
This SDK contains a number of custom link checks. These are designed to make the development process simpler and more integrated.
If at any time, they become too intrusive, they can easily switch off by including the Lint ID in the following block of your build.gradle:
android {
lintOptions {
disable {LINT_ISSUE_ID_1}, {LINT_ISSUE_ID_2}, {LINT_ISSUE_ID_3}...
}
}General
| Lint Issue ID | Description |
|---|---|
| MParticleVersionInconsistency | mParticle dependencies should, but do not have, matching versions |
| MParticleInitialization | mParticle.start() is not being called in Application.onCreate(), or may be being called multiple times |
| MParticleInstallRefReceiver | ReferrerReceiver is present, but has been removed |
Data Planning
| Lint Issue ID | Description |
|---|---|
| DataplanViolation | DataPlan violations |
| NodeMissing | The required node dependency is not present in the $PATH variable |
| DataPlanMissing | Unable to fetch you DataPlan, could be a problem with credentials or network connectivity |
Web
Our Web Linter lints JavaScript and TypeScript code.
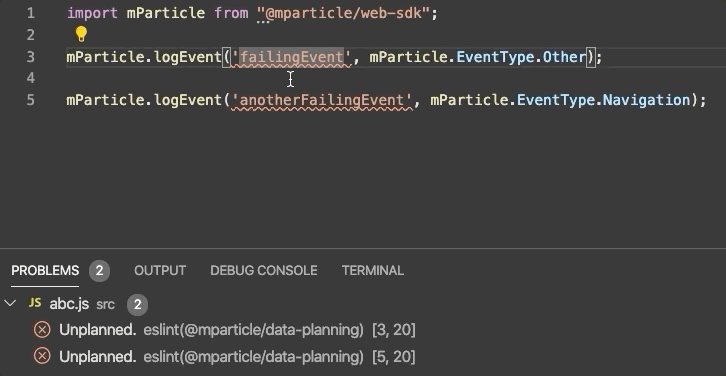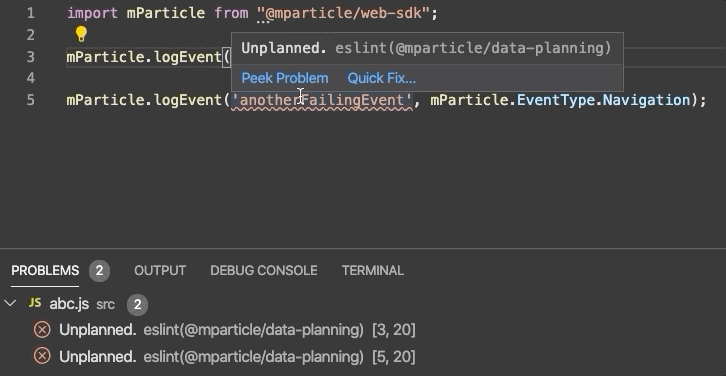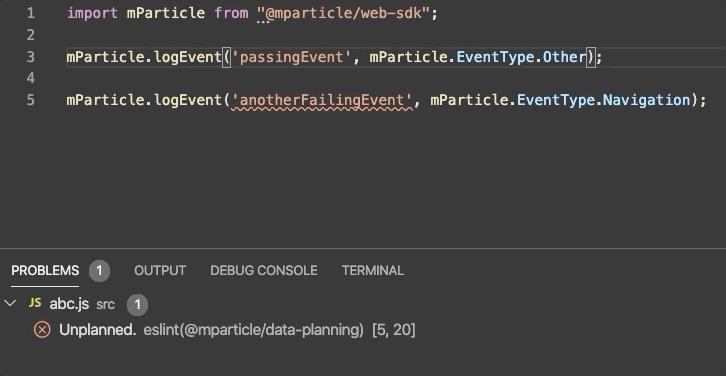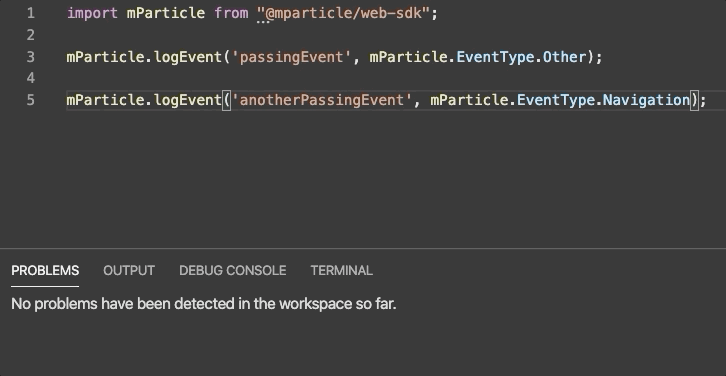
Our web linter is hosted on npm and is built on top of ESLint, a tool that is industry-standard for web development. It supports both JavaScript and TypeScript files. You’ll need an .eslintrc file as part of your ESLint setup.
Since the web data planning linter is built on top of ESLint, it can be used within continuous integration systems to warn or even fail builds due to data quality issues.
To get started, ensure you have a data plan downloaded and referenced properly in your mParticle config file.
Javascript
1. Install mParticle’s eslint plugin:
npm install --save-dev @mparticle/eslint-plugin2. Specify your Data Plan
If you haven’t already done so, download your data plan from the mParticle platform and save it to a file in your source repository. Reference this in the mp.config.jsonfile to tell the linter where to find the data plan file.
{
"planningConfig": {
"dataPlanVersionFile": "./plan.json"
}
}3. Setup .eslintrc file
Inside your .eslintrc file, add @mparticle/eslint-plugin to the plugins array, and plugin:@mparticle/data-planning to the extends array:
{
...
"plugins": ["@mparticle/eslint-plugin"],
"extends": ["plugin:@mparticle/data-planning"],
...
}You may have to restart your IDE for changes to take effect. If you are using VSCode, you can quickly do this by hitting CMD + Shift + P, typing reload, and executing Developer: Reload Window. Each time you update your data plan, reloading the IDE will allow the new data points to be consumed by the linter.
After you’ve followed the steps above, you can test the linter against your data plan. Events that are unplanned will be underlined to note that they should be fixed, as in the example in the beginning of this section.
TypeScript
Since our plugin is built on ESLint’s architecture, it also works with TypeScript (.ts) files, though two additional steps are required:
- If you are self-hosting, include
declare module "@mparticle/web-sdk"in your root folder’sindex.d.tsfile. npm install --save-dev @typescript-eslint/parserand include@typescript-eslint/parseras yourparserin your .eslintrc file:
{
"parser": "@typescript-eslint/parser",
"plugins": ["@mparticle/eslint-plugin"],
"extends": [
"plugin:@mparticle/data-planning"
]
}Was this page helpful?