Integrations
Data Warehouse
mParticle’s Data Warehouse integration with Amazon Redshift forwards all your incoming data to a Redshift cluster, allowing you to query the raw data directly.
The integration performs the following tasks in your Redshift cluster:
- Creates a table for each custom event name and each eCommerce event name with a volume above a defined threshold. Less common events are recorded in a single table, labeled
otherevents. - Adds new columns to tables when new events or user attributes are received.
- Creates a view unioning all tables within each schema, and a view in the PUBLIC schema that unions the views of all schema. Updates these views as new tables are created.
- If enabled, performs data hygeine on your cluster every 24 hours to purge expired data and run
vacuumandanalyzecommands.
By default, the integration begins loading current data into Redshift from the time it is enabled. You can work with your mParticle Customer Service Manager to load historical data.
Enable the Integration
Redshift Database Setup
1. Create a Database and Schema
Create your Redshift Database. The database should be in the same region as your mParticle pod. For example, if your mParticle pod is US1 or US2, create your Redshift database in us_east-1. Choosing a different region increases latency between mParticle and Redshift.
Within your database, create a schema to store your data.
2. Create groups and users to manage permissions
Once your database is ready, you need to create groups with permissions to read and write data to the database.
create group readwritegroup;
create group readonlygroup;
grant all on schema your_schema_name to group readwritegroup;Be sure to replace your_schema_name with your own name.
mParticle uses these groups to grant permissions for new tables it creates in the database. You must use the names readwritegroup and readonlygroup. You can also use these groups to control permissions for mParticle data in Redshift.
Create a user in each group. mParticle uses the dataloader user to create tables and write to the schema. The readonlyuser is used to run queries from the mParticle dashboard.
create user dataloader in group readwritegroup password 'Aabcde123!';
create user readonlyuser in group readonlygroup password 'Abcde123!';mParticle Setup
After adding Amazon Redshift from the integrations Directory, you can find the settings UI at Setup > Data Warehouse.
From the main page for your Redshift configuration, select the Settings tab to provide the necessary settings to get your Redshift integration working.
To forward data subject erasure requests to Amazon Redshift, set the Forwarding Status toggle to Active and select I understand after reading the disclaimer. Once the status has been set to Active, erasure requests are sent to Amazon Redshift immediately upon being received by mParticle.
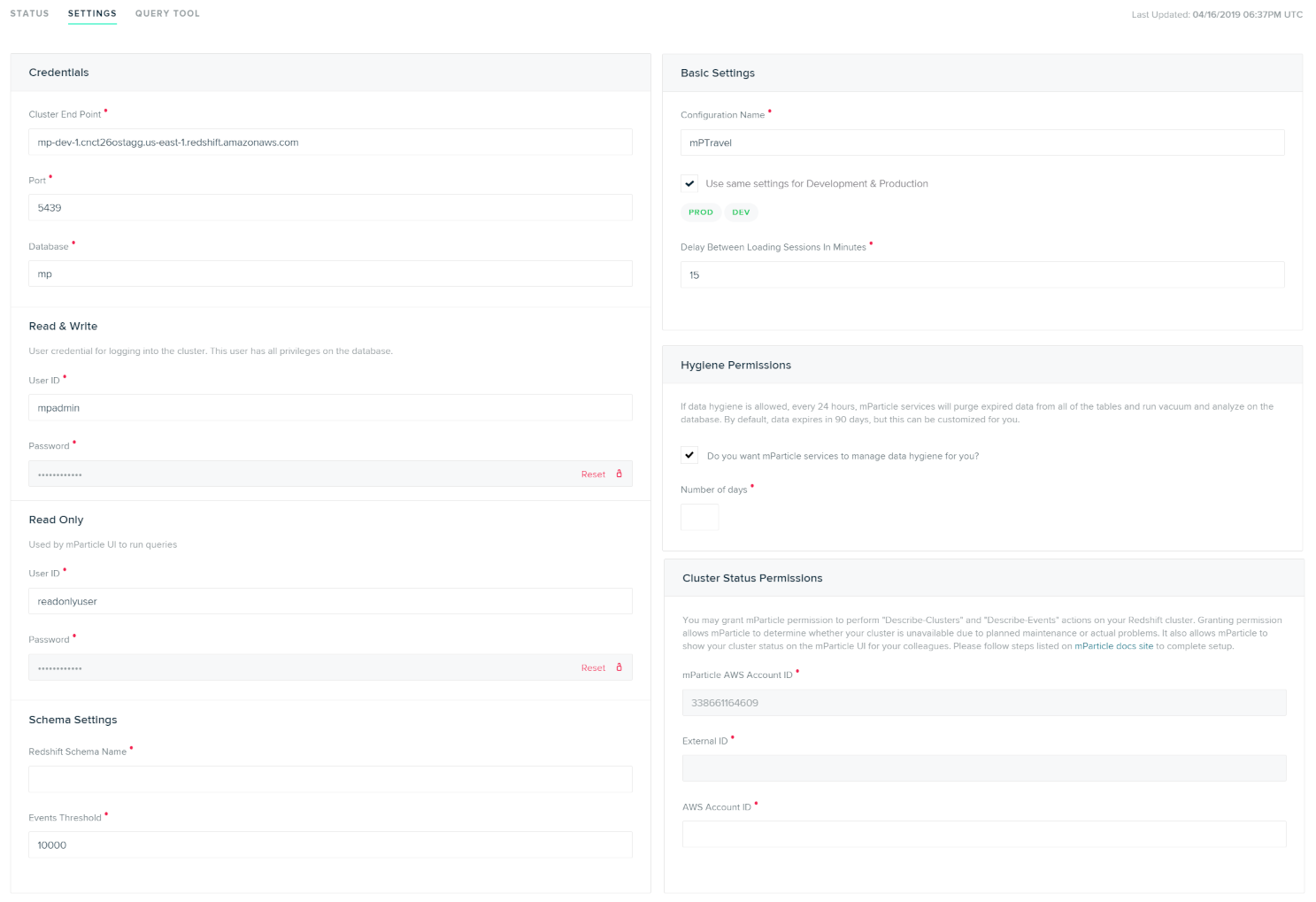
Configuration Settings
| Setting Name | Data Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster Endpoint | string |
Endpoint string shown on Configuration tab on your Redshift Dashboard. | |
| Port | number |
5439 | Open port for your cluster. You can find this on the details page for your cluster in Redshift. |
| Database | string |
The name of the database where you want to store mParticle Data. | |
| Read & Write User ID | string |
User ID for the dataloader user you created in your Redshift setup. These credentials will be used to manage the schema and load data. |
|
| Read & Write Password | string |
The password for the dataloader user. |
|
| Read Only User ID | string |
User ID for the readonlyuser user you created in your Redshift setup. These credentials will be used when running queries from the mParticle UI. |
|
| Read & Write Password | string |
The password for the readonlyuser user. |
|
| Redshift Schema Name | string |
Name of an existing schema where you want to store mParticle data. | |
| Events Threshold | number |
10000 | The number of times a custom or commerce event name must be received in 30 day period for mParticle to create a dedicated table for that event. |
| Delay Between Loading Sessions in Minutes | number |
15 | Allows you to adjust how often you want to load data into the data warehouse. Note that the minimum time is 1 minute and the maximum time is 24 hours (60 minutes x 24). |
| Send user attribute columns | bool |
true |
If enabled, individual columns are created for each user attribute |
| Store device stamp | bool |
false | Store device application stamp in the mParticleDeviceID column. Note that this change does not apply retroactively to tables that have already been created. Data deletion and a replay will be needed in order for existing tables to include this column. |
| Hygiene Permissions | bool |
true | If enabled, every 24 hours, mParticle will purge data over a certain age and perform vacuum and analyze commands on your database. |
| Number of Days | number |
90 | If Data Hygiene is enabled, this is the age in days past which data is purged. |
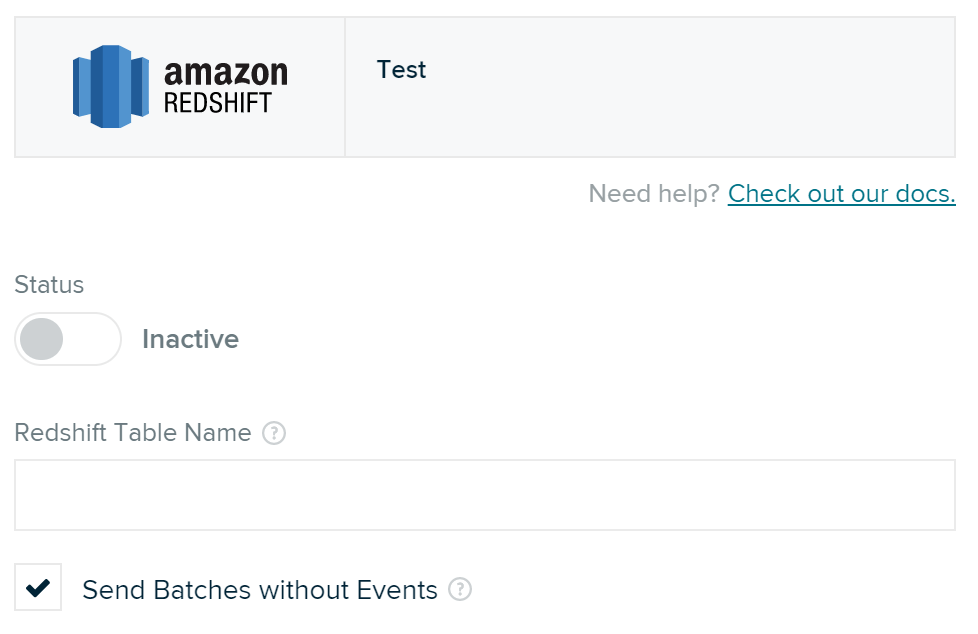
Once your Data Warehose integration is configured, connect individual inputs to the Amazon Redshift output from the Connections page. You must connect every input you want to store data for.
Connection Settings
| Setting Name | Data Type | Default Value | Platform | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redshift Table Name | string |
Out of Band | Table name for this partner feed. If not set, the partner name will be used. Only applicable to feeds inputs, no effect on apps inputs. If “Split Partner Feed Data by Event Name” checkbox is enabled, this setting is not used. | |
| Split Partner Feed Data by Event Name | boolean |
False | Out of Band | If enabled, split partner feed data by event name. Otherwise load data into the same table. |
| Send Batches without Events | boolean |
True | All | If enabled, an event batch that contains no events will be forwarded. |
Data Schema
Each common custom event name and eCommerce event name have their own table in Redshift, and all other event names (e.g., session-start, session-end) are stored in a single “otherevents” table. The naming conversion of the table names are as follows.
- A custom event name will have a table named event_[event type]_[event name]. For example, a custom event of event type Navigation named SignUp will have a table named event_navigation_signup.
- An eCommerce event name will have a table named ecomm_[event name].
- Consent events have tables named consent_given and consent_rejected
- All other events are stored in a table named otherevents.
mParticle also creates two views, which can be used to get aggregated views of your app data.
- Under each schema, a view called eventsview that unions all tables under the schema.
- Under the “public” schema, a view called eventsview that unions all eventsview views from all schema in the database.
Common Columns
Each table has the following common columns.
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AppId | int | mParticle app Id |
| AppPlatformId | int | mParticle AppPlatformId, e.g., Google Now app has iOS platform and Android platform, and each platform has an unique mParticle AppPlatformId |
| AppName | varchar(255) | App name |
| AppVersion | varchar(255) | App version |
| PackageName | varchar(255) | App package name |
| AppArchitecture | varchar(255) | App architecture |
| IsPirated | bool | Is the device pirated? |
| ApplicationBuildNumber | varchar(255) | Application build number |
| IsDebugSigning | bool | Is the app debug signing? |
| UpgradeDate | bigint | App upgrade timestamp |
| AppEnvironment | varchar(255) | App environment, debug or production |
| InstallReferrer | varchar(255) | Install referrer |
| Brand | varchar(255) | Device brand |
| Product | varchar(255) | Device product |
| DeviceName | varchar(255) | Device name |
| DeviceUdid | varchar(255) | Device UDID |
| Manufacturer | varchar(255) | Device manufacturer |
| Platform | varchar(255) | Device platform |
| OSVersion | varchar(255) | Device OS version |
| DeviceModel | varchar(255) | Device model |
| LocaleCountry | varchar(255) | Device’s locale country |
| LocaleLanguage | varchar(255) | Device’s locale language |
| NetworkCountry | varchar(255) | Network country |
| NetworkCarrier | varchar(255) | Network carrier name |
| ScreenHeight | int | Device’s screen height |
| ScreenWidth | int | Device’s screen width |
| ScreenDpi | int | Device’s screen dpi |
| DeviceUtcOffset | int | Device UTC offset |
| OsVersionInt | int | Android OS version int |
| Jailbroken | varchar(255) | Device’s jailbroken status |
| IDFA | varchar(255) | iOS IDFA |
| GoogleAID | varchar(255) | Android Google Advertising ID |
| Architecture | varchar(255) | Device architecture |
| IsTablet | bool | Is the device a tablet? |
| VendorIdentifier | varchar(255) | iOS vendor identifier |
| Pushtoken | varchar(255) | Push token |
| AttributionServiceProvider | varchar(255) | Attribution service provider name |
| AttributionPublisher | varchar(255) | Attributed publisher name |
| AttributionCampaign | varchar(255) | Attributed campaign name |
| mParticleUserId | bigint | UserId assigned by mParticle |
| CustomerId | varchar(255) | User’s customerID, usually this is the unique userId in your system |
| FacebookId | varchar(255) | User’s Facebook user Id |
| TwitterId | varchar(255) | User’s Twitter ID |
| GoogleUserId | varchar(255) | User’s Google ID |
| MicrosoftUserId | varchar(255) | User’s Microsoft ID |
| YahooUserId | varchar(255) | User’s Yahoo ID |
| varchar(255) | User’s email | |
| OtherUserId | varchar(255) | “Other” type user identity |
| IsDebug | bool | True for debug environment and false for production environment |
| BatchId | bigint | A unique ID of the batch |
| BatchTimestamp | bigint | Batch timestamp |
| SdkVersion | varchar(255) | mParticle SDK version |
| ClientIp | varchar(20) | Client IP address |
| ClientIpV6 | varchar(45) | Client IP address (compatible with v6) |
| GeoLookupInfo | varchar(1024) | Geo lookup information |
| entrypointtype | smallint | Type of incoming data, Type of incoming data, 1 means from SDK and 128 means from S2S |
| CountryCode | varchar(255) | Country code |
| CityName | varchar(255) | City name |
| PostalCode | varchar(255) | Postal code |
| RegionCode | varchar(255) | Geo region code |
| Latitude | double | Geo latitude |
| Longitude | double | Geo longitude |
| Accuracy | double | Geo accuracy |
| AudienceMembership | varchar(2048) | A array of mParticle segment ID’s the user was a member of at the time of the event |
| SessionId | bigint | A unique ID of the session |
| SessionStartTimestamp | bigint | Session start timestamp |
| EventId | bigint | A unique ID of the event |
| EventTimestamp | bigint | Event timestamp |
| MessageTypeId | int | Message Type Id 1 = Session Start 2 = Session End 3 = Screen View 4 = App Event 5 = Crash Report 6 = Opt Out 7 = First Run 8 = PreAttribution 9 = Push Registration 10 = Application State Transition 11 = Push Message 12 = Network Performance 13 = Breadcrumb 14 = Profile 15 = Push Reaction 16 = Commerce Event 17 = UserAttributeChange 18 = UserIdentityChange 19 = Uninstall |
| EventStartTimestamp | bigint | Event start timestamp |
| EventDate | date | Event date. Sort key |
| EventHour | datetime | Event hour. Sort key |
| EventName | varchar(255) | Event name |
| EventTypeId | int | Event type Id |
| EventLength | bigint | How long did the event take? Represents session length in milliseconds on session end events |
| EventLtvValue | double | Monetary value extracted from the event |
| DataConnectionType | varchar(255) | Data connection type |
| ExceptionHandled | bool | Handled exception or crash |
| IsFirstRunEvent | bool | Is this a first run event? |
| FirstSeenTimestamp | bigint | Timestamp of the first event on this user |
| IsUpgradeEvent | bool | Is this an app upgrade event? |
| SuccessfullyClosed | bool | Is the last session successfully closed? Will be false if app is forcefully killed |
| ApplicationTransitionTypeId | smallint | Application Transition TypeId. AppInit = 1 AppExit = 2 AppBackground = 3 AppForeground = 4 |
| eventcustomflags | varchar(2048) | Event custom flags |
| EventAttributes | varchar(10240) | A JSON string that contains key/value pairs of event attribute names and values |
| UserAttributes | varchar(10240) | A JSON string that contains key/value pairs of user attribute names and values |
eCommerce Only Columns
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ProductActionTypeId | smallint | eCommerce Product Action Type Id 0 = unknown 1 = add_to_cart 2 = remove_from_cart 3 = checkout 4 = checkout_option 5 = click 6 = view_detail 7 = purchase 8 = refund 9 = add_to_wishlist 10 = remove_from_wishlist |
| EcommerceScreenName | varchar(50) | eCommerce screen name |
| EcommerceIsNonInteractive | bool | Is eCommerce action interactive? |
| PromotionActionTypeId | smallint | Promotion Action Type Id 0 = unknown 1 = view 2 = click |
| ProductAction | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing product action details |
| PromotionAction | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing promotion action details |
| ProductImpressions | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing product impressions |
| ShoppingCart | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing shopping cart info |
Event and User Attribute Columns
Each individual event name table (not including otherevents) also has one column per event attribute, named like: “ea[attribute_name]”, and one column per user attribute, named like “ua[attribute_name]“.
The benefit of these individual attribute columns is that you don’t have to use slower JSON parse functions in your query to extract attribute values from either EventAttributes or UserAttributes columns. If you wish, individual User Attribute columns can be turned off by disabling the Send user attribute columns setting.
Partner Feed Data
Events from each connected Partner Feed will be stored under a single table unless the Split Partner Feed Data by Event Name checkbox is enabled. You can choose the table name for each Feed in the Connection Settings.
Device Application Stamp Forwarding
Events can be forwarded with a Device Application Stamp stored in the device ID column. You can enable this in the settings page for your data warehouse configuration by toggling the Store Device Stamp checkbox.
Error Handling
mParticle loads data into Redshift via Amazon S3 and can tolerate the Redshift cluster being unavailable for up to 30 days, depending on data volume. In the event of extended downtime on your cluster, a data replay can be arranged.
Was this page helpful?