Documentation
Developers
API References
Platform API
Platform API Overview
Accounts
Apps
Audiences
Calculated Attributes
Data Points
Feeds
Field Transformations
Services
Users
Workspaces
Data Subject Request API
Data Subject Request API Version 1 and 2
Data Subject Request API Version 3
Warehouse Sync API
Warehouse Sync API Overview
Warehouse Sync API Tutorial
Warehouse Sync API Reference
Data Mapping
Warehouse Sync SQL Reference
Warehouse Sync Troubleshooting Guide
ComposeID
Warehouse Sync API v2 Migration
Calculated Attributes Seeding API
Bulk Profile Deletion API Reference
Custom Access Roles API
Data Planning API
Group Identity API Reference
Pixel Service
Profile API
Events API
mParticle JSON Schema Reference
IDSync
Client SDKs
AMP
AMP SDK
Android
Initialization
Configuration
Network Security Configuration
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Screen Events
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Push Notifications
WebView Integration
Logger
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Linting Data Plans
Troubleshooting the Android SDK
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 5
Cordova
Cordova Plugin
Identity
Direct Url Routing
Direct URL Routing FAQ
Web
Android
iOS
iOS
Initialization
Configuration
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Screen Tracking
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Push Notifications
Webview Integration
Upload Frequency
App Extensions
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Linting Data Plans
Troubleshooting iOS SDK
Social Networks
iOS 14 Guide
iOS 15 FAQ
iOS 16 FAQ
iOS 17 FAQ
iOS 18 FAQ
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 7
React Native
Getting Started
Identity
Unity
Upload Frequency
Getting Started
Opt Out
Initialize the SDK
Event Tracking
Commerce Tracking
Error Tracking
Screen Tracking
Identity
Location Tracking
Session Management
Web
Initialization
Configuration
Content Security Policy
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Page View Tracking
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Custom Logger
Persistence
Native Web Views
Self-Hosting
Multiple Instances
Web SDK via Google Tag Manager
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Facebook Instant Articles
Troubleshooting the Web SDK
Browser Compatibility
Linting Data Plans
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 2 of the SDK
Xamarin
Getting Started
Identity
Web
Alexa
Server SDKs
Node SDK
Go SDK
Python SDK
Ruby SDK
Java SDK
Quickstart
Android
Overview
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Verify your input
Step 3. Set up your output
Step 4. Create a connection
Step 5. Verify your connection
Step 6. Track events
Step 7. Track user data
Step 8. Create a data plan
Step 9. Test your local app
iOS Quick Start
Overview
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Verify your input
Step 3. Set up your output
Step 4. Create a connection
Step 5. Verify your connection
Step 6. Track events
Step 7. Track user data
Step 8. Create a data plan
Python Quick Start
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Create an output
Step 3. Verify output
Guides
Partners
Introduction
Outbound Integrations
Outbound Integrations
Firehose Java SDK
Inbound Integrations
Compose ID
Data Hosting Locations
Glossary
Migrate from Segment to mParticle
Migrate from Segment to mParticle
Migrate from Segment to Client-side mParticle
Migrate from Segment to Server-side mParticle
Segment-to-mParticle Migration Reference
Rules Developer Guide
API Credential Management
The Developer's Guided Journey to mParticle
Guides
Getting Started
Create an Input
Start capturing data
Connect an Event Output
Create an Audience
Connect an Audience Output
Transform and Enhance Your Data
Personalization
Introduction
Profiles
Audiences
Audiences Overview
Create an Audience
Connect an Audience
Manage Audiences
Real-time Audiences (Legacy)
Standard Audiences (Legacy)
Calculated Attributes
Calculated Attributes Overview
Using Calculated Attributes
Create with AI Assistance
Calculated Attributes Reference
Predictive Audiences
Predictive Audiences Overview
Using Predictive Audiences
Journeys
Journeys Overview
Manage Journeys
Download an audience from a journey
Audience A/B testing from a journey
Journeys 2.0
Predictive Attributes
What are predictive attributes?
Platform Guide
Billing
Usage and Billing Report
The New mParticle Experience
The new mParticle Experience
The Overview Map
Observability
Observability Overview
Observability User Guide
Observability Troubleshooting Examples
Observability Span Glossary
Introduction
Data Retention
Connections
Activity
Live Stream
Data Filter
Rules
Tiered Events
mParticle Users and Roles
Analytics Free Trial
Troubleshooting mParticle
Usage metering for value-based pricing (VBP)
Analytics
Introduction
Setup
Sync and Activate Analytics User Segments in mParticle
User Segment Activation
Welcome Page Announcements
Settings
Project Settings
Roles and Teammates
Organization Settings
Global Project Filters
Portfolio Analytics
Analytics Data Manager
Analytics Data Manager Overview
Events
Event Properties
User Properties
Revenue Mapping
Export Data
UTM Guide
Query Builder
Data Dictionary
Query Builder Overview
Modify Filters With And/Or Clauses
Query-time Sampling
Query Notes
Filter Where Clauses
Event vs. User Properties
Group By Clauses
Annotations
Cross-tool Compatibility
Apply All for Filter Where Clauses
Date Range and Time Settings Overview
User Attributes at Event Time
Understanding the Screen View Event
Analyses
Analyses Introduction
Segmentation: Basics
Getting Started
Visualization Options
For Clauses
Date Range and Time Settings
Calculator
Numerical Settings
Segmentation: Advanced
Assisted Analysis
Properties Explorer
Frequency in Segmentation
Trends in Segmentation
Did [not] Perform Clauses
Cumulative vs. Non-Cumulative Analysis in Segmentation
Total Count of vs. Users Who Performed
Save Your Segmentation Analysis
Export Results in Segmentation
Explore Users from Segmentation
Funnels: Basics
Getting Started with Funnels
Group By Settings
Conversion Window
Tracking Properties
Date Range and Time Settings
Visualization Options
Interpreting a Funnel Analysis
Funnels: Advanced
Group By
Filters
Conversion over Time
Conversion Order
Trends
Funnel Direction
Multi-path Funnels
Analyze as Cohort from Funnel
Save a Funnel Analysis
Explore Users from a Funnel
Export Results from a Funnel
Saved Analyses
Manage Analyses in Dashboards
Dashboards
Dashboards––Getting Started
Manage Dashboards
Dashboard Filters
Organize Dashboards
Scheduled Reports
Favorites
Time and Interval Settings in Dashboards
Query Notes in Dashboards
User Aliasing
Analytics Resources
The Demo Environment
Keyboard Shortcuts
Tutorials
Analytics for Marketers
Analytics for Product Managers
Compare Conversion Across Acquisition Sources
Analyze Product Feature Usage
Identify Points of User Friction
Time-based Subscription Analysis
Dashboard Tips and Tricks
Understand Product Stickiness
Optimize User Flow with A/B Testing
User Segments
IDSync
IDSync Overview
Use Cases for IDSync
Components of IDSync
Store and Organize User Data
Identify Users
Default IDSync Configuration
Profile Conversion Strategy
Profile Link Strategy
Profile Isolation Strategy
Best Match Strategy
Aliasing
Data Master
Group Identity
Overview
Create and Manage Group Definitions
Introduction
Catalog
Live Stream
Data Plans
Data Plans
Blocked Data Backfill Guide
Warehouse Sync
Data Privacy Controls
Data Subject Requests
Default Service Limits
Feeds
Cross-Account Audience Sharing
Approved Sub-Processors
Import Data with CSV Files
Import Data with CSV Files
CSV File Reference
Glossary
Video Index
Analytics (Deprecated)
Identity Providers
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Setup Examples
Introduction
Developer Docs
Introduction
Integrations
Introduction
Rudderstack
Google Tag Manager
Segment
Data Warehouses and Data Lakes
Advanced Data Warehouse Settings
AWS Kinesis (Snowplow)
AWS Redshift (Define Your Own Schema)
AWS S3 Integration (Define Your Own Schema)
AWS S3 (Snowplow Schema)
BigQuery (Snowplow Schema)
BigQuery Firebase Schema
BigQuery (Define Your Own Schema)
GCP BigQuery Export
Snowflake (Snowplow Schema)
Snowplow Schema Overview
Snowflake (Define Your Own Schema)
Developer Basics
Aliasing
Dashboard Filters
Dashboard filters allow you to set date and event property filters at the top of a dashboard that simultaneously affect all analyses within that dashboard. This means you can avoid manually editing each widget on a dashboard to update filters, and realize benefits like:
- Greater Efficiency: Users can now save time previously spent manually adjusting filters on each analysis separately.
- Consistency: With consistent filters applied across a dashboard, there is a reduced risk of discrepancies in data interpretation and analyses across a dashboard.
- Improved decision making: By providing a more unified view of filtered data, teams can make quicker decisions based on the most relevant and up-to-date information.
- Enhanced collaboration: When everyone is viewing the same filtered data, teams can make faster and more informed decisions.
Here is how to get started with Dashboard Filters.
Hide / show filters
Dashboard filters are displayed in the top row of a dashboard above the analyses, and they are shown by default. To hide the dashboard filters row, select Hide Filters in the top settings bar. To show them again, select Show Filters.
Date range filter
The date filter at the top of your dashboard lets you set a date range across all analyses within that dashboard. By default, there is no date range applied to a dashboard when it is created. The data displayed for each analysis reflects the date range set at the analysis level.
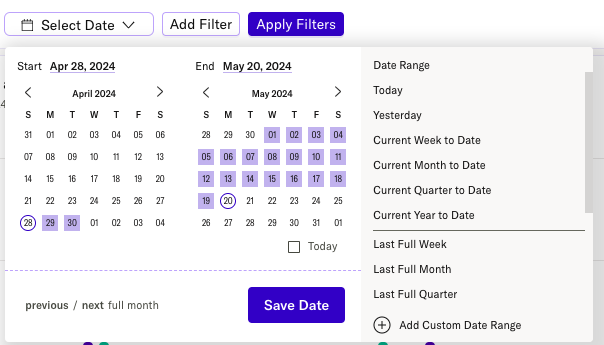
Set a date range for your dashboard
Click “Select Date” to expose the date selector. Here, you can choose a custom or preset date range.
Property filter
You can apply event property filters across all analyses on your dashboard. To do this, first select Add Filter to expose the event property query builder:
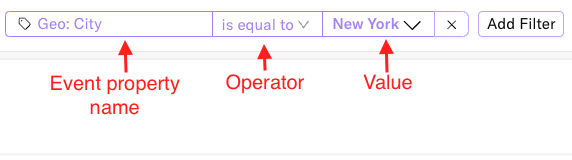
The query builder contains three components:
- Event Property (category and name): Select the event property you want to apply as a filter. The query builder organizes events into categories, so select the category first, followed by the event itself.
- Operator: Choose an operator for evaluating the logic in your filter. The default operator is is equal to, but you can change this to any other operator that is available to that the event property you have selected.
- Value: Provide a valid value for your chosen event property.
You can continue stringing filters together to hone in on a precise subset of your users. For example, applying the filter settings below to a dashboard will result in all analyses displaying data from the last full month where City is equal to New York, Subscription Plan is equal to Monthly, and Browser Name is equal to Chrome.

Remove a filter
To remove a filter from your query, click the “X” icon to the right of the filter description. This will remove that single filter from your query.
Apply filters
Each time you add or remove a new filter your query, you must select Apply Filters for your changes to be reflected in the dashboard. After applying filters, there will be a delay before the filtered data is loading. The loading state is indicated by spinning to the right of the title of each analysis widget.
![]()
Impact of dashboard filters at analysis level
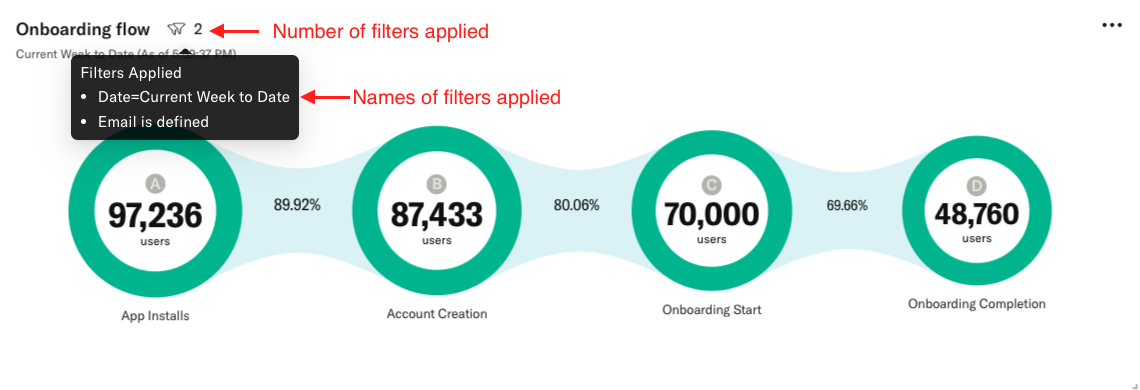
Each dashboard filter will be applied to the individual analyses within the dashboard, provided the filter and filter value are available within the analysis. Once you have applied filters to a dashboard, each analysis will display a filter icon in the bottom right indicating how many of the filters are applied at the level of that analysis. The names of the filters applied to this analysis will appear on hover:
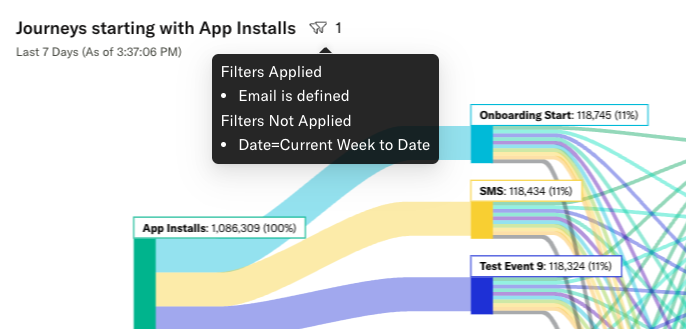
In cases where filters you’ve set at the dashboard level do not apply to an analysis, both the applied and unapplied filters will appear on hover:
When do dashboard filters apply to individual analyses?
Dashboard filters override analysis-level filters, provided the event property is available at the analysis level. For example, if a dashboard includes the filter State=CA as a filter, and an analysis within this dashboard has access to this property but is not using it as a filter, the analysis will have the filter State=CA applied once the dashboard-level filters are applied.
When do dashboard filters override analysis filters?
If a filter applied at the dashboard has been previously applied at the analysis level, the dashboard filter will override the analysis filter at analysis level. For example, if an analysis in a dashboard has the filter State=CA, and you apply a filter at the dashboard level saying State=MN, the dashboard filter will override the analysis filter, and the State will be updated to MN at the analysis level.
When are dashboard filters not applied at the dashboard level?
When a dashboard filter value does not exist in any of the analyses in that dashboard, this filter will not be applied at the dashboard level. For example, if you set a date range of 90 days on a dashboard that includes only Journeys, this filter will not be applied, since the lookback period for Journeys is 30 days.
Modifying dashboard filters at the analysis level When you modify a filter on an analysis that was set at the dashboard level, the change will persist in the underlying query, but will not impact the original dashboard filter. For example, say you have a dashboard with the geo filter State=New York, and you open an analysis on this dashboard on which that filter is applied. If you change that filter to State=California at the analysis level, the analysis will have State=California while the filter at the dashboard level will continue to be State=New York.
Open Query
This option opens the query with the most recent dashboard filters applied.
Open Query without Filters Applied
This option disregards any dashboard filters. It will display the results based on the filters applied previously on the analysis.
Managing filter updates across teammates
Dashboard filters include checks to ensure smooth collaboration between members of the same organization. Here are some of the scenarios these checks account for:
Another user has recently made changes to the dashboard
When viewing a dashboard for the first time after someone else in your organization has updated the filters, you will see a banner at the top of the dashboard indicating this:

In these cases, you will need to refresh the page to reflect the most recent filters before you are able to apply additional changes you have made to the dashboard filters.
Dashboard filters user access
Dashboard filters mirror dashboard-level and project-level permissions:
At the dashboard level:
- Edit privileges: Any user who can edit a dashboard can also edit that dashboard’s filters.
- View privileges: Any user who can only view a restricted dashboard has read-only privileges at the dashboard level. These users can view but not edit that dashboard’s filters.
At the project level:
Within project settings, users can be assigned one of three dashboard permission levels: Full, View, or None.
- Full: Any user with Full access at the project level can view and edit all dashboards, including their filters.
- View: Users with View project-level permissions have read-only access to dashboards, and can view but not edit dashboard filters.
- None: Users whose project-level permission is set to None may not view or edit dashboards within the project.
Optimize dashboard performance
You can optimize the performance of your dashboards by adhering to best practices when creating and filtering them, as well as when building the analyses they contain. Learn more here.
Was this page helpful?
- Last Updated: February 27, 2025