Developers
API References
Data Subject Request API
Data Subject Request API Version 1 and 2
Data Subject Request API Version 3
Platform API
Key Management
Platform API Overview
Accounts
Apps
Audiences
Calculated Attributes
Data Points
Feeds
Field Transformations
Services
Users
Workspaces
Warehouse Sync API
Warehouse Sync API Overview
Warehouse Sync API Tutorial
Warehouse Sync API Reference
Data Mapping
Warehouse Sync SQL Reference
Warehouse Sync Troubleshooting Guide
ComposeID
Warehouse Sync API v2 Migration
Bulk Profile Deletion API Reference
Calculated Attributes Seeding API
Custom Access Roles API
Data Planning API
Group Identity API Reference
Pixel Service
Profile API
Events API
mParticle JSON Schema Reference
IDSync
Client SDKs
AMP
AMP SDK
Android
Initialization
Configuration
Network Security Configuration
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Screen Events
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Push Notifications
WebView Integration
Logger
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Linting Data Plans
Troubleshooting the Android SDK
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 5
Cordova
Cordova Plugin
Identity
Direct Url Routing
Direct URL Routing FAQ
Web
Android
iOS
iOS
Workspace Switching
Initialization
Configuration
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Screen Tracking
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Push Notifications
Webview Integration
Upload Frequency
App Extensions
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Linting Data Plans
Troubleshooting iOS SDK
Social Networks
iOS 14 Guide
iOS 15 FAQ
iOS 16 FAQ
iOS 17 FAQ
iOS 18 FAQ
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 7
React Native
Getting Started
Identity
Unity
Upload Frequency
Getting Started
Opt Out
Initialize the SDK
Event Tracking
Commerce Tracking
Error Tracking
Screen Tracking
Identity
Location Tracking
Session Management
Web
Initialization
Configuration
Content Security Policy
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Page View Tracking
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Custom Logger
Persistence
Native Web Views
Self-Hosting
Multiple Instances
Web SDK via Google Tag Manager
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Facebook Instant Articles
Troubleshooting the Web SDK
Browser Compatibility
Linting Data Plans
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 2 of the SDK
Xamarin
Getting Started
Identity
Alexa
Server SDKs
Node SDK
Go SDK
Python SDK
Ruby SDK
Java SDK
Quickstart
Android
Overview
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Verify your input
Step 3. Set up your output
Step 4. Create a connection
Step 5. Verify your connection
Step 6. Track events
Step 7. Track user data
Step 8. Create a data plan
Step 9. Test your local app
iOS Quick Start
Overview
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Verify your input
Step 3. Set up your output
Step 4. Create a connection
Step 5. Verify your connection
Step 6. Track events
Step 7. Track user data
Step 8. Create a data plan
Python Quick Start
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Create an output
Step 3. Verify output
Guides
Partners
Introduction
Outbound Integrations
Outbound Integrations
Firehose Java SDK
Inbound Integrations
Compose ID
Data Hosting Locations
Glossary
Rules Developer Guide
API Credential Management
The Developer's Guided Journey to mParticle
Guides
Customer 360
Overview
User Profiles
Overview
User Profiles
Group Identity
Overview
Create and Manage Group Definitions
Calculated Attributes
Calculated Attributes Overview
Using Calculated Attributes
Create with AI Assistance
Calculated Attributes Reference
Predictive Attributes
What are predictive attributes?
Getting Started
Create an Input
Start capturing data
Connect an Event Output
Create an Audience
Connect an Audience Output
Transform and Enhance Your Data
Segmentation
New Audiences Experience
Audiences Overview
Create an Audience
Connect an Audience
Manage Audiences
FAQ
Classic Audiences Experience
Real-time Audiences (Legacy)
Standard Audiences (Legacy)
New vs. Classic Experience Comparison
Predictive Audiences
Predictive Audiences Overview
Using Predictive Audiences
Platform Guide
Billing
Usage and Billing Report
The New mParticle Experience
The new mParticle Experience
The Overview Map
Observability
Observability Overview
Observability User Guide
Observability Troubleshooting Examples
Observability Span Glossary
Platform Settings
Key Management
Event Forwarding
Notification Center (Early Access)
System Alerts
Trends
Introduction
Data Retention
Data Catalog
Connections
Activity
Data Plans
Live Stream
Filters
Rules
Blocked Data Backfill Guide
Tiered Events
mParticle Users and Roles
Analytics Free Trial
Troubleshooting mParticle
Usage metering for value-based pricing (VBP)
IDSync
IDSync Overview
Use Cases for IDSync
Components of IDSync
Store and Organize User Data
Identify Users
Default IDSync Configuration
Profile Conversion Strategy
Profile Link Strategy
Profile Isolation Strategy
Best Match Strategy
Aliasing
Analytics
Introduction
Core Analytics (Beta)
Setup
Sync and Activate Analytics User Segments in mParticle
User Segment Activation
Welcome Page Announcements
Settings
Project Settings
Roles and Teammates
Organization Settings
Global Project Filters
Portfolio Analytics
Analytics Data Manager
Analytics Data Manager Overview
Events
Event Properties
User Properties
Revenue Mapping
Export Data
UTM Guide
Analyses
Analyses Introduction
Segmentation: Basics
Getting Started
Visualization Options
For Clauses
Date Range and Time Settings
Calculator
Numerical Settings
Segmentation: Advanced
Assisted Analysis
Properties Explorer
Frequency in Segmentation
Trends in Segmentation
Did [not] Perform Clauses
Cumulative vs. Non-Cumulative Analysis in Segmentation
Total Count of vs. Users Who Performed
Save Your Segmentation Analysis
Export Results in Segmentation
Explore Users from Segmentation
Funnels: Basics
Getting Started with Funnels
Group By Settings
Conversion Window
Tracking Properties
Date Range and Time Settings
Visualization Options
Interpreting a Funnel Analysis
Funnels: Advanced
Group By
Filters
Conversion over Time
Conversion Order
Trends
Funnel Direction
Multi-path Funnels
Analyze as Cohort from Funnel
Save a Funnel Analysis
Explore Users from a Funnel
Export Results from a Funnel
Saved Analyses
Manage Analyses in Dashboards
Query Builder
Data Dictionary
Query Builder Overview
Modify Filters With And/Or Clauses
Query-time Sampling
Query Notes
Filter Where Clauses
Event vs. User Properties
Group By Clauses
Annotations
Cross-tool Compatibility
Apply All for Filter Where Clauses
Date Range and Time Settings Overview
User Attributes at Event Time
Understanding the Screen View Event
User Aliasing
Dashboards
Dashboards––Getting Started
Manage Dashboards
Dashboard Filters
Organize Dashboards
Scheduled Reports
Favorites
Time and Interval Settings in Dashboards
Query Notes in Dashboards
Analytics Resources
The Demo Environment
Keyboard Shortcuts
User Segments
Warehouse Sync
Data Privacy Controls
Data Subject Requests
Default Service Limits
Feeds
Cross-Account Audience Sharing
Approved Sub-Processors
Import Data with CSV Files
Import Data with CSV Files
CSV File Reference
Glossary
Video Index
Analytics (Deprecated)
Identity Providers
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Setup Examples
Introduction
Developer Docs
Introduction
Integrations
Introduction
Rudderstack
Google Tag Manager
Segment
Data Warehouses and Data Lakes
Advanced Data Warehouse Settings
AWS Kinesis (Snowplow)
AWS Redshift (Define Your Own Schema)
AWS S3 Integration (Define Your Own Schema)
AWS S3 (Snowplow Schema)
BigQuery (Snowplow Schema)
BigQuery Firebase Schema
BigQuery (Define Your Own Schema)
GCP BigQuery Export
Snowflake (Snowplow Schema)
Snowplow Schema Overview
Snowflake (Define Your Own Schema)
Developer Basics
Aliasing
Integrations
24i
Event
Aarki
Audience
Abakus
Event
Actable
Feed
ABTasty
Audience
AdChemix
Event
AdMedia
Audience
Adobe Audience Manager
Audience
Adobe Marketing Cloud
Cookie Sync
Server-to-Server Events
Platform SDK Events
Adobe Target
Audience
Adobe Campaign Manager
Audience
AdPredictive
Feed
AgilOne
Event
Algolia
Event
Amazon Advertising
Audience
Alooma
Event
Amazon Kinesis
Event
Amazon Redshift
Data Warehouse
Amazon S3
Event
Amazon SNS
Event
Amobee
Audience
Amazon SQS
Event
Anodot
Event
Antavo
Feed
Apptentive
Event
Apptimize
Event
Apteligent
Event
Attractor
Event
Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
Event
Awin
Event
Bidease
Audience
Bing Ads
Event
Bluecore
Event
Bluedot
Feed
Branch S2S Event
Event
Bugsnag
Event
Cadent
Audience
Census
Feed
Conversant
Event
comScore
Event
Crossing Minds
Event
Custom Feed
Custom Feed
Datadog
Event
Databricks
Data Warehouse
Didomi
Event
Dynalyst
Audience
Edge226
Audience
Emarsys
Audience
Epsilon
Event
Everflow
Audience
Facebook Offline Conversions
Event
Google Analytics for Firebase
Event
Flurry
Event
Flybits
Event
ForeSee
Event
FreeWheel Data Suite
Audience
Friendbuy
Event
Google Ad Manager
Audience
Google Analytics
Event
Google Analytics 4
Event
Google BigQuery
Audience
Data Warehouse
Google Enhanced Conversions
Event
Google Marketing Platform
Cookie Sync
Audience
Event
Google Marketing Platform Offline Conversions
Event
Google Pub/Sub
Event
Google Tag Manager
Event
Heap
Event
Herow
Feed
Hightouch
Feed
Hyperlocology
Event
Impact
Event
Ibotta
Event
InMarket
Audience
ID5
Kit
Intercom
Event
Inspectlet
Event
ironSource
Audience
Kafka
Event
Kissmetrics
Event
Kubit
Event
LaunchDarkly
Feed
LifeStreet
Audience
LiveLike
Event
Liveramp
Audience
Localytics
Event
MadHive
Audience
mAdme Technologies
Event
Marigold
Audience
Mediasmart
Audience
MediaMath
Audience
Microsoft Azure Event Hubs
Event
Mintegral
Audience
Monetate
Event
Movable Ink - V2
Event
Movable Ink
Event
Multiplied
Event
Nami ML
Feed
Nanigans
Event
NCR Aloha
Event
Neura
Event
OneTrust
Event
Oracle BlueKai
Event
Paytronix
Feed
Persona.ly
Audience
Personify XP
Event
Plarin
Event
Quadratic Labs
Event
Qualtrics
Event
Quantcast
Event
Rakuten
Event
Regal
Event
Reveal Mobile
Event
RevenueCat
Feed
Salesforce Mobile Push
Event
Salesforce Sales and Service Cloud
Event
Scalarr
Event
Shopify
Feed
Custom Pixel
Signal
Event
SimpleReach
Event
Singular-DEPRECATED
Event
Skyhook
Event
Slack
Event
Smadex
Audience
SmarterHQ
Event
Snowflake
Data Warehouse
Snapchat Conversions
Event
Snowplow
Event
Splunk MINT
Event
StartApp
Audience
Talon.One
Audience
Event
Feed
Loyalty Feed
Tapad
Audience
Tapjoy
Audience
Taptica
Audience
Taplytics
Event
Teak
Audience
The Trade Desk
Cookie Sync
Audience
Event
Ticketure
Feed
TUNE
Event
Triton Digital
Audience
Valid
Event
Vkontakte
Audience
Vungle
Audience
Webhook
Event
Webtrends
Event
White Label Loyalty
Event
Wootric
Event
Xandr
Audience
Cookie Sync
Yahoo (formerly Verizon Media)
Cookie Sync
Audience
Yotpo
Feed
YouAppi
Audience
Primer
Event
Data Privacy Controls
Manage your consent and opt-out privacy obligations under the GDPR and CCPA with Data Privacy Controls. This feature is not prescriptive and there is no single way to implement consent or opt-out. Instead, mParticle gives you a simple, standard technique for storing and applying consent and opt-out choices. Consent state powers both GDPR consent and CCPA data sale opt-out.
This guide introduces you to mParticle’s data privacy control functionality and shows you how to collect an individual’s consent and apply it to your data flows.
Common uses of data privacy controls
Data privacy controls are flexible and customizable, allowing you to build any data flow or consent-based logic you need.
Use mParticle’s data privacy controls to help comply with CCPA’s “do not sell my data” requirement by collecting users who opt-out and blocking those users’ data from flowing to any ‘data sale’ output by:
- Recording a CCPA data sale opt-out as a user consent (more information below)
- Identify which outputs count as ‘data sale’ and apply the below forwarding rule to them
- Applying a forwarding rule of: Do not forward if CCPA Data sale opt out is present
GDPR defines consent as one method of lawful data processing. One common setup is to:
- Define a processing purpose of ‘marketing’
- Prompt users for affirmative consent for ‘marketing’
- Identify which outputs would perform ‘analytics’ processing
- Apply a forwarding rule of: Only forward user data if GDPR Consent for ‘marketing’ is true
Data privacy and the mParticle platform
Once enabled and configured, data privacy work with the mParticle platform to ingest and pass on consent state:
- Define categories of data collection called consent purposes.
- Store the consent state in a user’s profile.
- Control data flow based on stored consent.
- Send user consent state to your integrations (outputs).
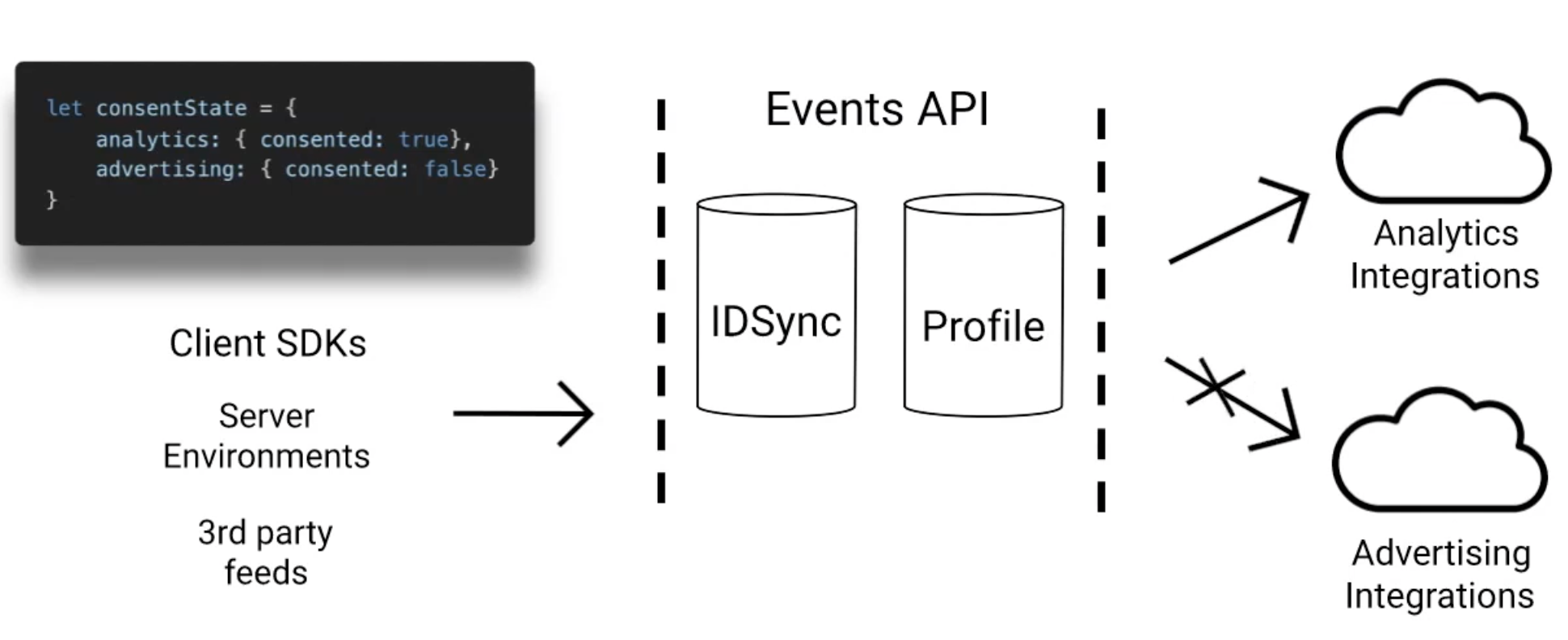
Enabling data privacy controls
Data privacy controls save user consent decisions and applies them to data flows.
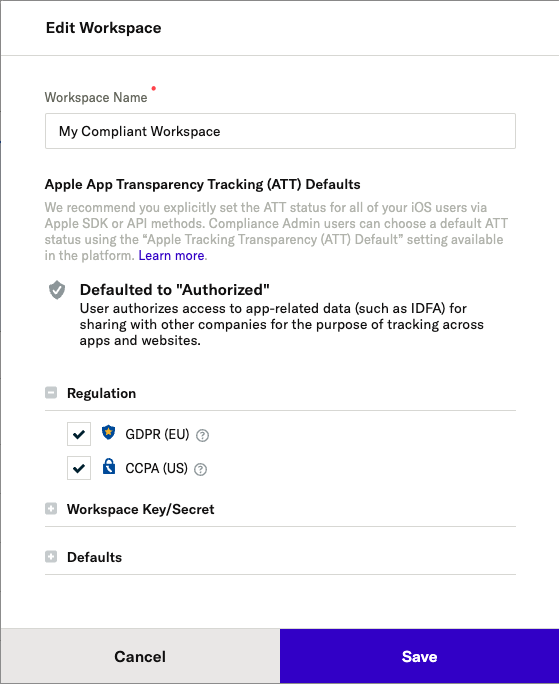
- To enable GDPR and/or CCPA compliance features for a workspace, hover your cursor over the Settings icon in the left nav and click Workspaces. Select a workspace from the list, and click Regulation.
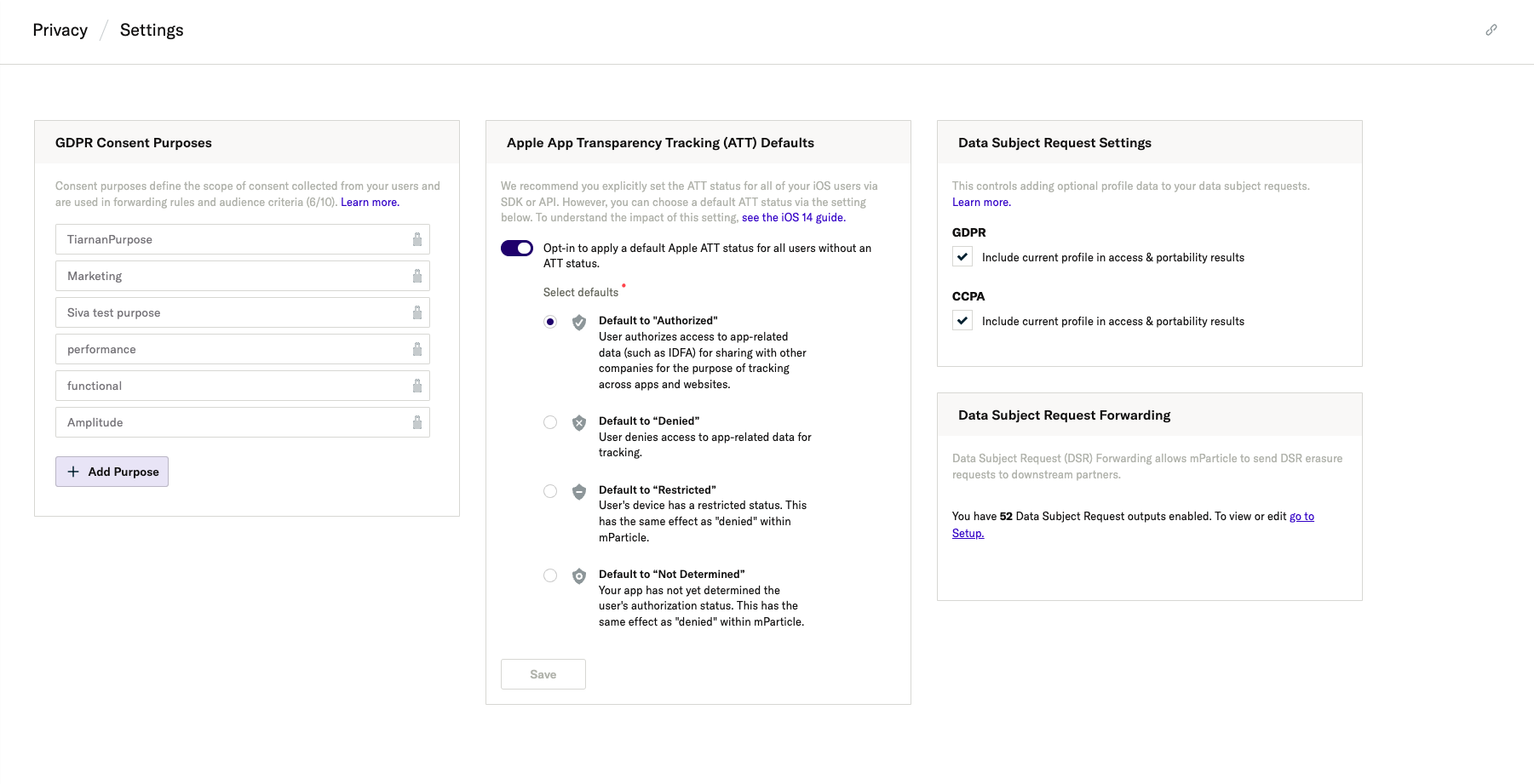
- For GDPR, create a set of purposes from Privacy > Privacy Settings in the dashboard.
- For CCPA, once it is enabled in your workspace, the purpose
data_sale_opt_outis automatically created. The SDKs and mParticle UIs facilitate using this purpose, so you don’t need to hardcode it anywhere.
Consent properties
The mParticle format for a single record of a user decision on a privacy prompt, .consent, is our consent_state object. This is used for both GDPR-style opt-in consent and for CCPA-style opt-out.
For each user or workspace, consent state can be stored for each possible combination of regulation and purpose. For each purpose, the following fields are supported.
All fields are optional, except consented, timestamp_unixtime_ms, regulation and purpose. The regulation and purpose fields are built into the structure. Be sure to include your privacy and compliance experts when deciding how to implement optional fields.
Property |
Type, Required |
Example Values |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| regulation | string Required |
gdpr |
The regulation under which a user consent or preference is being saved. Currently gdpr and ccpa are supported. |
|
| purpose | string Required |
geolocation |
A data processing purpose that describes the type of processing done on the data subject’s data. For GDPR, purposes must be defined in mParticle before using them in a consent_state object. For CCPA, this is not required as the default CCPA purpose is data_sale_opt_out |
|
| consented | bool Required |
true / false |
For GDPR, this records the user’s decision on the prompted consent purpose. If the user agreed (true) or rejected (false). For CCPA, set this to true if the user has opted-out of data sale and false if they have not opted-out of data sale. |
|
| timestamp_unixtime_ms | number Required |
1510949166 |
A timestamp for the creation of the consent state. mParticle’s SDKs send this field automatically. If using the HTTP API, this field must be set manually. | |
| document | string Not required |
"v23.2b" |
An identifier for the document, document version or experience that the user may have consented to. | |
| location | string Not required |
"example.com/", "17 Cherry Tree Lane" |
A location where the user gave consent. This property exists only to provide additional context. It may be a physical or digital location. | |
| hardware_id | string Required |
"IDFA:a5d934n0-232f-4afc-2e9a-3832d95zc702" |
A hardware ID for the device or browser used to give consent. This property exists only to provide additional context and is not used to identify users. |
Example consent state
Consent state can be logged via the HTTP API simply by including a consent state object in a batch, mirroring the structure of the user profile (above):
"consent_state": {
"gdpr": {
"location_collection": {
"document": "location_collection_agreement.v43",
"consented": true,
"timestamp_unixtime_ms": 1523039002083,
"location": "dtmgbank.com/signup",
"hardware_id": "IDFA:a5d934n0-232f-4afc-2e9a-3832d95zc702"
},
"parental": {
"document": "standard_parental_consent.v2",
"consented": true,
"timestamp_unixtime_ms": 1523039002083,
"location": "dtmgbank.com/signup",
"hardware_id": "IDFA:a5d934n0-232f-4afc-2e9a-3832d95zc702"
}
},
"ccpa":{
"data_sale_opt_out":{
"consented": true,
"timestamp_unixtime_ms": 1579198790480
}
}
}Collecting consent state
For detailed definitions of how to report consent state, review the sections of our API and SDK references that cover data privacy controls:
Additionally, our integration with OneTrust allows you to ingest customer consent states into mParticle.
Using consent state
User profiles
Consent state is maintained per person on the User Profile using the structure defined above.
For testing consent, you can use User Activity View to check that a consent was recorded correctly. Here is an example of how CCPA data sale opt-out will appear:

Audiences
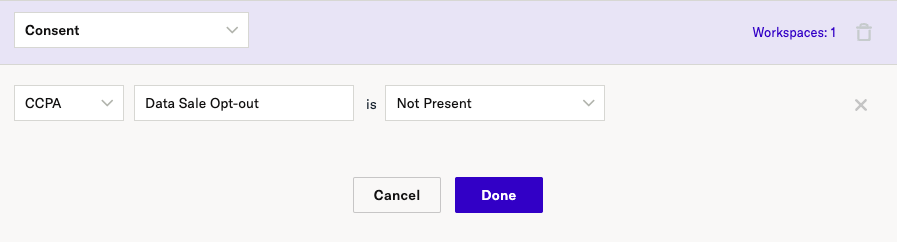
Consent state can be used to create conditions in the Audience Builder to check a users’ consent state as a requirement for audience inclusion or exclusion.
For example, for CCPA you may want to include only users who have NOT opted out of data sale, by adding a criteria like this:
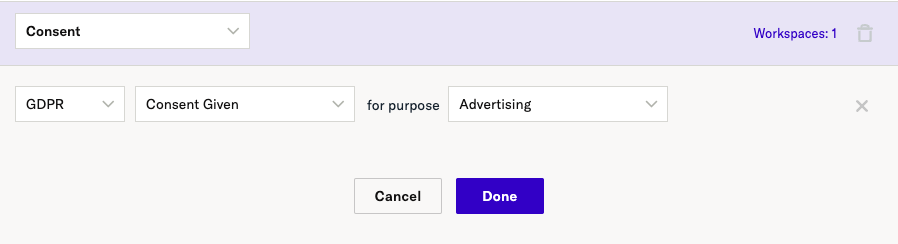
For GDPR, you may want to include only users that have an opt-in consent for a given purpose, shown here as ‘Advertising’:
Connections and forwarding rules
Consent state can be used to create forwarding rules that selectively filter data based on a users consent state, in real time and per-person.
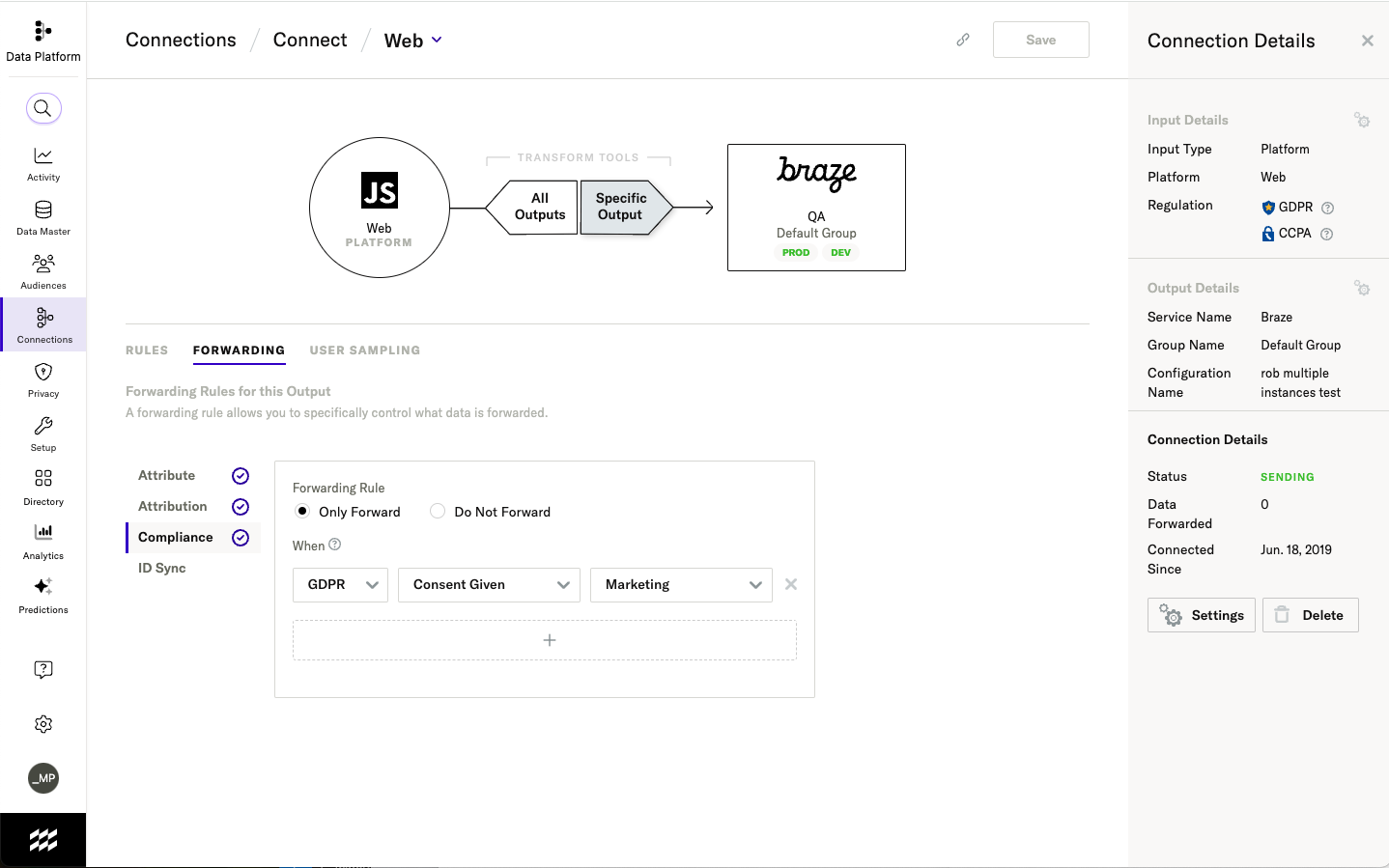
For example, you can choose to only forward data from users who have given consent for a particular purpose.
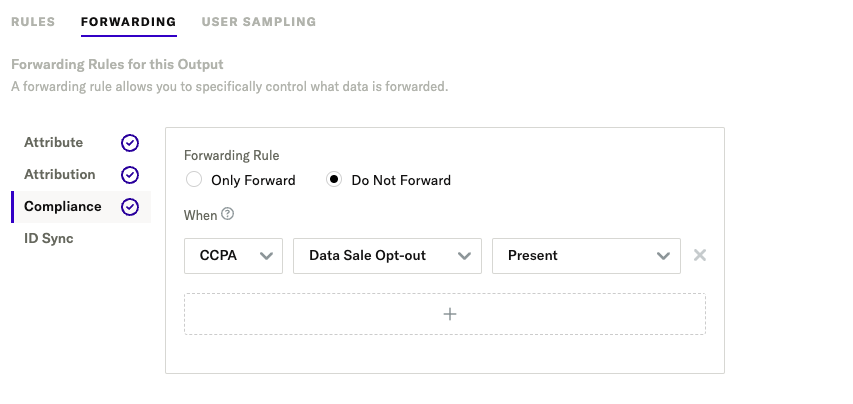
For CCPA, you may want a forwarding rule to apply a data sale opt-out. In this example, users’ who have a consent state of true for the CCPA purpose of data_sale_opt_out will NOT have their data forwarded (if the consent state is missing or false for that purpose, data will flow):
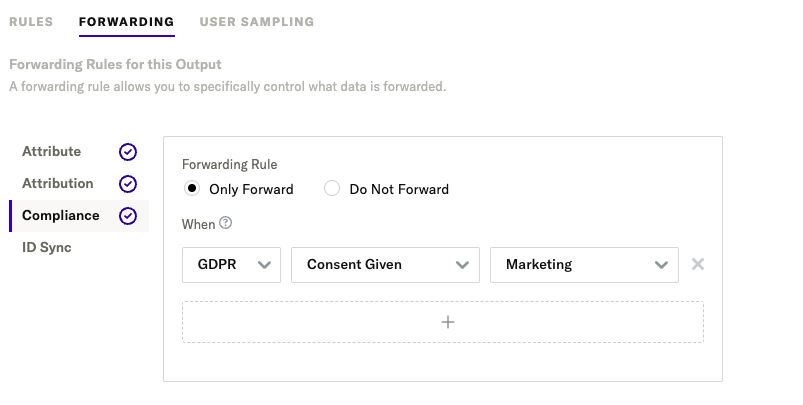
For GDPR, you may want a forwarding rule to only send data when a single purpose is consented:
Kits and forwarding rules
If you set up a Forwarding Rule for an embedded kit integration, the iOS and Android SDKs will check consent status for the user on initialization. If the rule condition fails, the kit will not be initialized. Note that kits are only initialized when a session begins or on user change, so if consent status changes in the course of a session, while mParticle will immediately stop forwarding data to the kit, it is possible that an embedded kit may remain active and independently forwarding data to a partner from the client until the session ends.
Forwarding consent state to partners
When the consent state of a profile changes, that change can be communicated to mParticle event integrations. If the consent_state object on an incoming event batch contains changes from the existing profile, mParticle adds a ‘system notification’ to the batch for each consent state change before the batch is sent to incoming forwarders. This notification contains the full old and new consent state objects:
"system_notifications": [
{
"data": {
"purpose": "location_collection",
"current": {
"regulation": "GDPR",
"document": "location_collection_agreement_v4",
"consented": false,
"timestamp_unixtime_ms": 1523045332033,
"location": "17 Cherry Tree Lane",
"hardware_id": "IDFA:a5d934n0-232f-4afc-2e9a-3832d95zc702"
},
"old": {
"regulation": "GDPR",
"document": "location_collection_agreement_v4",
"consented": true,
"timestamp_unixtime_ms": 1523039002083,
"location": "17 Cherry Tree Lane",
"hardware_id": "IDFA:a5d934n0-232f-4afc-2e9a-3832d95zc702"
}
},
"type": "gdpr_change"
}
]There are currently two ways that consent state changes are forwarded to mParticle event integrations:
-
Some partners accept raw event batch data from mParticle, mostly for data storage or custom analytics use cases. For these partners, mParticle will forward the ‘system_notifications’ object with each relevant event batch. Forwarding of system notifications can be turned off with a user setting. Integrations that can currently receive the system notifications object include:
-
mParticle is working with other partners to support forwarding consent state changes as a Custom Event. These events contain the new consent state information as custom attributes, a custom event type of
"Consent", and an event name of"Consent Given"or"Consent Rejected". These consent events are forwarded to supporting partners as standard custom events.{ "data": { "event_name": "Consent Given", "custom_event_type": "Consent", "custom_attributes": { "consented": "true", "document": "location_collection_agreement_v4", "hardware_id": "IDFA:a5d934n0-232f-4afc-2e9a-3832d95zc702", "purpose": "location_collection", "location": "17 Cherry Tree Lane", "regulation": "GDPR", "timestamp_unixtime_ms": 1523039002083 }, "event_type": "custom_event" } }Partners that currently accept these custom consent state events include:
“GDPR Consent Change” is listed as a data type in the Integrations directory and we will update this list as more partners add support. Please reach out to your success manager if you would like to distribute consent to an additional partner.
Data subject requests
mParticle helps you respond to data subject requests as mandated by the GDPR and CCPA regulations.
You can search for integrations that support data subject requests in the Integrations page. Search on category Data Subject Request.
Ingest GPC signals
The California Consumer Protection Act (CCPA) and the upcoming CPRA (California Privacy Rights Act) require that users can signal their privacy choices. In support of that requirement, you can ingest Global Privacy Control (GPC) signals with mParticle.
Browsers append the GPC signal to HTTP requests and make it queryable via the DOM. This signal is designed to convey a person’s request to websites and services to not sell or share their personal information with third parties, per the Global Privacy Control specification. This opt-out is at the browser level, allowing users to turn on the GPC signal for all or specific websites.
The workflow for ingesting and forwarding GPC signals via SDK or Events API:
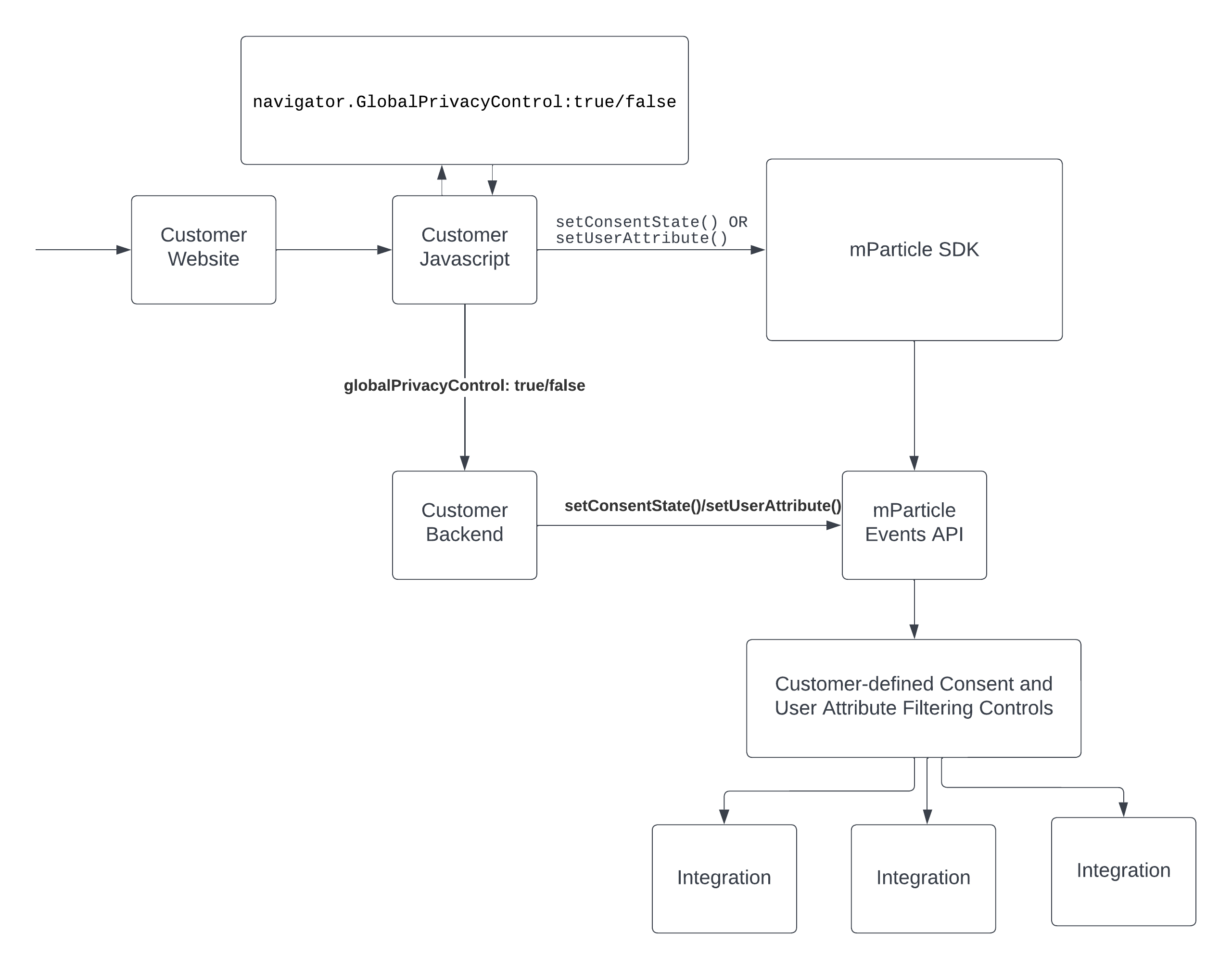
Sample code for GPC
This sample code show two options: mapping to a GDPR purpose and mapping to a user attribute.
/*
First, grab the GPC signal. "true" indicates the user has signaled an opt-out
See here for more details on querying the GPC signal:
https://globalprivacycontrol.github.io/gpc-spec/
*/
var gpcSignal = navigator.globalPrivacyControl;
/*
Option 1:
In this example, the GPC signal is mapped to a "targeting_collection" GDPR purpose.
This is only an example, you determine the GDPR purposes and how GPC maps to them.
You can do the same mapping to CPPA.
*/
var targeting_consent = mParticle.Consent.createGDPRConsent(
!gpcSignal, // note that this is inverted
Date.now(), // Timestamp
"browser_gpc_signal", // Document
"17 Cherry Tree Lane", // Location
"browser-id:a5d934n0-232f-4afc-2e9a-3832d95zc702" // Hardware ID
);
// Add to your consent state
var consentState = mParticle.Consent.createConsentState();
consentState.addGDPRConsentState("targeting_collection", targeting_consent);
var user = mParticle.Identity.getCurrentUser();
user.setConsentState(consentState);
/*
Option 2:
In this example, the GPC signal is mapped to a user attribute
*/
var user = mParticle.Identity.getCurrentUser();
user.setUserAttribute("gpc_signal", gpcSignal);Was this page helpful?
- Last Updated: July 3, 2025