Developers
API References
Data Subject Request API
Data Subject Request API Version 1 and 2
Data Subject Request API Version 3
Platform API
Key Management
Platform API Overview
Accounts
Apps
Audiences
Calculated Attributes
Data Points
Feeds
Field Transformations
Services
Users
Workspaces
Warehouse Sync API
Warehouse Sync API Overview
Warehouse Sync API Tutorial
Warehouse Sync API Reference
Data Mapping
Warehouse Sync SQL Reference
Warehouse Sync Troubleshooting Guide
ComposeID
Warehouse Sync API v2 Migration
Audit Logs API
Bulk Profile Deletion API Reference
Calculated Attributes Seeding API
Custom Access Roles API
Data Planning API
Group Identity API Reference
Pixel Service
Profile API
Events API
mParticle JSON Schema Reference
IDSync
Client SDKs
AMP
AMP SDK
Cordova
Cordova Plugin
Identity
Android
Initialization
Configuration
Network Security Configuration
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Screen Events
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Push Notifications
WebView Integration
Logger
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Workspace Switching
Linting Data Plans
Troubleshooting the Android SDK
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 5
Direct Url Routing
Direct URL Routing FAQ
Web
Android
iOS
iOS
Workspace Switching
Initialization
Configuration
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Screen Tracking
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Push Notifications
Webview Integration
Upload Frequency
App Extensions
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Linting Data Plans
Troubleshooting iOS SDK
Social Networks
iOS 14 Guide
iOS 15 FAQ
iOS 16 FAQ
iOS 17 FAQ
iOS 18 FAQ
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 7
React Native
Getting Started
Identity
Unity
Upload Frequency
Getting Started
Opt Out
Initialize the SDK
Event Tracking
Commerce Tracking
Error Tracking
Screen Tracking
Identity
Location Tracking
Session Management
Web
Initialization
Configuration
Content Security Policy
Event Tracking
User Attributes
IDSync
Page View Tracking
Commerce Events
Location Tracking
Media
Kits
Application State and Session Management
Data Privacy Controls
Error Tracking
Opt Out
Custom Logger
Persistence
Native Web Views
Self-Hosting
Multiple Instances
Web SDK via Google Tag Manager
Preventing Blocked HTTP Traffic with CNAME
Facebook Instant Articles
Troubleshooting the Web SDK
Browser Compatibility
Linting Data Plans
API Reference
Upgrade to Version 2 of the SDK
Xamarin
Getting Started
Identity
Alexa
Quickstart
Android
Overview
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Verify your input
Step 3. Set up your output
Step 4. Create a connection
Step 5. Verify your connection
Step 6. Track events
Step 7. Track user data
Step 8. Create a data plan
Step 9. Test your local app
iOS Quick Start
Overview
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Verify your input
Step 3. Set up your output
Step 4. Create a connection
Step 5. Verify your connection
Step 6. Track events
Step 7. Track user data
Step 8. Create a data plan
Python Quick Start
Step 1. Create an input
Step 2. Create an output
Step 3. Verify output
Server SDKs
Node SDK
Go SDK
Python SDK
Ruby SDK
Java SDK
Guides
Partners
Introduction
Outbound Integrations
Outbound Integrations
Firehose Java SDK
Inbound Integrations
Compose ID
Data Hosting Locations
Glossary
Migrate from Segment to mParticle
Migrate from Segment to mParticle
Migrate from Segment to Client-side mParticle
Migrate from Segment to Server-side mParticle
Segment-to-mParticle Migration Reference
Rules Developer Guide
API Credential Management
The Developer's Guided Journey to mParticle
Guides
Composable Audiences
Composable Audiences Overview
User Guide
User Guide Overview
Warehouse Setup
Warehouse Setup Overview
Audience Setup
Frequently Asked Questions
Customer 360
Overview
User Profiles
Overview
User Profiles
Group Identity
Overview
Create and Manage Group Definitions
Calculated Attributes
Calculated Attributes Overview
Using Calculated Attributes
Create with AI Assistance
Calculated Attributes Reference
Predictions
Predictions Overview
What's Changed in the New Predictions UI
View and Manage Predictions
Identity Dashboard (Early Access)
Getting Started
Create an Input
Start capturing data
Connect an Event Output
Create an Audience
Connect an Audience Output
Transform and Enhance Your Data
Platform Guide
Billing
Usage and Billing Report
The New mParticle Experience
The new mParticle Experience
The Overview Map
Observability
Observability Overview
Observability User Guide
Observability Troubleshooting Examples
Observability Span Glossary
Platform Settings
Audit Logs
Key Management
Platform Configuration
Event Forwarding
Event Match Quality Dashboard
Notifications
System Alerts
Trends
Introduction
Data Retention
Data Catalog
Connections
Activity
Data Plans
Live Stream
Filters
Rules
Blocked Data Backfill Guide
Tiered Events
mParticle Users and Roles
Analytics Free Trial
Troubleshooting mParticle
Usage metering for value-based pricing (VBP)
IDSync
IDSync Overview
Use Cases for IDSync
Components of IDSync
Store and Organize User Data
Identify Users
Default IDSync Configuration
Profile Conversion Strategy
Profile Link Strategy
Profile Isolation Strategy
Best Match Strategy
Aliasing
Segmentation
Audiences
Audiences Overview
Create an Audience
Connect an Audience
Manage Audiences
Audience Sharing
Match Boost
FAQ
Inclusive & Exclusive Audiences (Early Access)
Inclusive & Exclusive Audiences Overview
Using Logic Blocks in Audiences
Combining Inclusive and Exclusive Audiences
Inclusive & Exclusive Audiences FAQ
Classic Audiences
Standard Audiences (Legacy)
Predictive Audiences
Predictive Audiences Overview
Using Predictive Audiences
New vs. Classic Experience Comparison
Analytics
Introduction
Core Analytics (Beta)
Setup
Sync and Activate Analytics User Segments in mParticle
User Segment Activation
Welcome Page Announcements
Settings
Project Settings
Roles and Teammates
Organization Settings
Global Project Filters
Portfolio Analytics
Analytics Data Manager
Analytics Data Manager Overview
Events
Event Properties
User Properties
Revenue Mapping
Export Data
UTM Guide
Analyses
Analyses Introduction
Segmentation: Basics
Getting Started
Visualization Options
For Clauses
Date Range and Time Settings
Calculator
Numerical Settings
Segmentation: Advanced
Assisted Analysis
Properties Explorer
Frequency in Segmentation
Trends in Segmentation
Did [not] Perform Clauses
Cumulative vs. Non-Cumulative Analysis in Segmentation
Total Count of vs. Users Who Performed
Save Your Segmentation Analysis
Export Results in Segmentation
Explore Users from Segmentation
Funnels: Basics
Getting Started with Funnels
Group By Settings
Conversion Window
Tracking Properties
Date Range and Time Settings
Visualization Options
Interpreting a Funnel Analysis
Funnels: Advanced
Group By
Filters
Conversion over Time
Conversion Order
Trends
Funnel Direction
Multi-path Funnels
Analyze as Cohort from Funnel
Save a Funnel Analysis
Explore Users from a Funnel
Export Results from a Funnel
Saved Analyses
Manage Analyses in Dashboards
Query Builder
Data Dictionary
Query Builder Overview
Modify Filters With And/Or Clauses
Query-time Sampling
Query Notes
Filter Where Clauses
Event vs. User Properties
Group By Clauses
Annotations
Cross-tool Compatibility
Apply All for Filter Where Clauses
Date Range and Time Settings Overview
User Attributes at Event Time
Understanding the Screen View Event
User Aliasing
Dashboards
Dashboards––Getting Started
Manage Dashboards
Organize Dashboards
Dashboard Filters
Scheduled Reports
Favorites
Time and Interval Settings in Dashboards
Query Notes in Dashboards
Analytics Resources
The Demo Environment
Keyboard Shortcuts
User Segments
Data Privacy Controls
Data Subject Requests
Default Service Limits
Feeds
Cross-Account Audience Sharing
Import Data with CSV Files
Import Data with CSV Files
CSV File Reference
Glossary
Video Index
Analytics (Deprecated)
Identity Providers
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Setup Examples
Introduction
Developer Docs
Introduction
Integrations
Introduction
Rudderstack
Google Tag Manager
Segment
Data Warehouses and Data Lakes
AWS Kinesis (Snowplow)
Advanced Data Warehouse Settings
AWS Redshift (Define Your Own Schema)
AWS S3 Integration (Define Your Own Schema)
AWS S3 (Snowplow Schema)
BigQuery (Snowplow Schema)
BigQuery Firebase Schema
BigQuery (Define Your Own Schema)
GCP BigQuery Export
Snowflake (Snowplow Schema)
Snowplow Schema Overview
Snowflake (Define Your Own Schema)
Developer Basics
Aliasing
Integrations
24i
Event
Aarki
Audience
ABTasty
Audience
Actable
Feed
AdChemix
Event
Adobe Marketing Cloud
Cookie Sync
Server-to-Server Events
Platform SDK Events
AdMedia
Audience
Adobe Audience Manager
Audience
Adobe Experience Platform
Event
Adobe Campaign Manager
Audience
Adobe Target
Audience
AdPredictive
Feed
AgilOne
Event
Algolia
Event
Amazon Advertising
Audience
Amazon Kinesis
Event
Amazon Redshift
Data Warehouse
Amazon S3
Event
Amazon SNS
Event
Amobee
Audience
Amazon SQS
Event
Anodot
Event
Antavo
Feed
Apptentive
Event
Apptimize
Event
Awin
Event
Apteligent
Event
Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
Event
Bidease
Audience
Bluecore
Event
Bing Ads
Event
Bluedot
Feed
Branch S2S Event
Event
Bugsnag
Event
Cadent
Audience
Census
Feed
comScore
Event
Conversant
Event
Crossing Minds
Event
Custom Feed
Custom Feed
Databricks
Data Warehouse
Didomi
Event
Datadog
Event
Eagle Eye
Audience
Emarsys
Audience
Edge226
Audience
Everflow
Audience
Epsilon
Event
Facebook Offline Conversions
Event
Google Analytics for Firebase
Event
Flybits
Event
Flurry
Event
ForeSee
Event
Friendbuy
Event
FreeWheel Data Suite
Audience
Google Analytics
Event
Google Ad Manager
Audience
Google Analytics 4
Event
Google BigQuery
Audience
Data Warehouse
Google Enhanced Conversions
Event
Google Marketing Platform
Audience
Cookie Sync
Event
Google Marketing Platform Offline Conversions
Event
Google Pub/Sub
Event
Google Tag Manager
Event
Herow
Feed
Heap
Event
Hightouch
Feed
Hyperlocology
Event
Ibotta
Event
ID5
Kit
Impact
Event
InMarket
Audience
Inspectlet
Event
Intercom
Event
ironSource
Audience
Kafka
Event
Kissmetrics
Event
Kubit
Event
LaunchDarkly
Feed
LifeStreet
Audience
LiveLike
Event
Liveramp
Audience
Localytics
Event
mAdme Technologies
Event
Marigold
Audience
MadHive
Audience
MediaMath
Audience
Microsoft Ads
Microsoft Ads Audience Integration
Mediasmart
Audience
Microsoft Azure Event Hubs
Event
Mintegral
Audience
Movable Ink
Event
Monetate
Event
Movable Ink - V2
Event
Multiplied
Event
Nami ML
Feed
NCR Aloha
Event
Nanigans
Event
OneTrust
Event
Neura
Event
Oracle BlueKai
Event
Paytronix
Feed
Personify XP
Event
Persona.ly
Audience
Primer
Event
Plarin
Event
Qualtrics
Event
Quantcast
Event
Rakuten
Event
Reveal Mobile
Event
RevenueCat
Feed
Salesforce Mobile Push
Event
Scalarr
Event
SimpleReach
Event
Shopify
Custom Pixel
Feed
Singular-DEPRECATED
Event
Slack
Event
Smadex
Audience
SmarterHQ
Event
Skyhook
Event
Snapchat Conversions
Event
Snowflake
Audience
Data Warehouse
Snowplow
Event
Splunk MINT
Event
StartApp
Audience
Talon.One
Audience
Event
Loyalty Feed
Feed
Tapad
Audience
Tapjoy
Audience
Taplytics
Event
Teak
Audience
Taptica
Audience
The Trade Desk
Audience
Cookie Sync
Event
Ticketure
Feed
Triton Digital
Audience
TUNE
Event
Valid
Event
Vkontakte
Audience
Vungle
Audience
Webhook
Event
Webtrends
Event
White Label Loyalty
Event
Wootric
Event
Xandr
Audience
Cookie Sync
Yahoo (formerly Verizon Media)
Audience
Cookie Sync
Yotpo
Feed
YouAppi
Audience
Regal
Event
Data Warehouse
mParticle’s Data Warehouse integration with Amazon Redshift forwards all your incoming data to a Redshift cluster, allowing you to query the raw data directly.
The integration performs the following tasks in your Redshift cluster:
- Creates a table for each custom event name and each eCommerce event name with a volume above a defined threshold. Less common events are recorded in a single table, labeled
otherevents. - Adds new columns to tables when new events or user attributes are received.
- Creates a view unioning all tables within each schema, and a view in the PUBLIC schema that unions the views of all schema. Updates these views as new tables are created.
- If enabled, performs data hygeine on your cluster every 24 hours to purge expired data and run
vacuumandanalyzecommands.
By default, the integration begins loading current data into Redshift from the time it is enabled. You can work with your mParticle Customer Service Manager to load historical data.
Enable the Integration
Redshift Database Setup
1. Create a Database and Schema
Create your Redshift Database. The database should be in the same region as your mParticle pod. For example, if your mParticle pod is US1 or US2, create your Redshift database in us_east-1. Choosing a different region increases latency between mParticle and Redshift.
Within your database, create a schema to store your data.
2. Create groups and users to manage permissions
Once your database is ready, you need to create groups with permissions to read and write data to the database.
create group readwritegroup;
create group readonlygroup;
grant all on schema your_schema_name to group readwritegroup;Be sure to replace your_schema_name with your own name.
mParticle uses these groups to grant permissions for new tables it creates in the database. You must use the names readwritegroup and readonlygroup. You can also use these groups to control permissions for mParticle data in Redshift.
Create a user in each group. mParticle uses the dataloader user to create tables and write to the schema. The readonlyuser is used to run queries from the mParticle dashboard.
create user dataloader in group readwritegroup password 'Aabcde123!';
create user readonlyuser in group readonlygroup password 'Abcde123!';mParticle Setup
After adding Amazon Redshift from the integrations Directory, you can find your integration settings by navigating to Data Platform > Setup > Outputs, selecting the Data Warehouse tab, and then selecting your new Redshift configuration.
From the main page for your Redshift configuration, select the Settings tab to provide the necessary settings to get your Redshift integration working.
To forward data subject erasure requests to Amazon Redshift, set the Forwarding Status toggle to Active and select I understand after reading the disclaimer. Once the status has been set to Active, erasure requests are sent to Amazon Redshift immediately upon being received by mParticle.
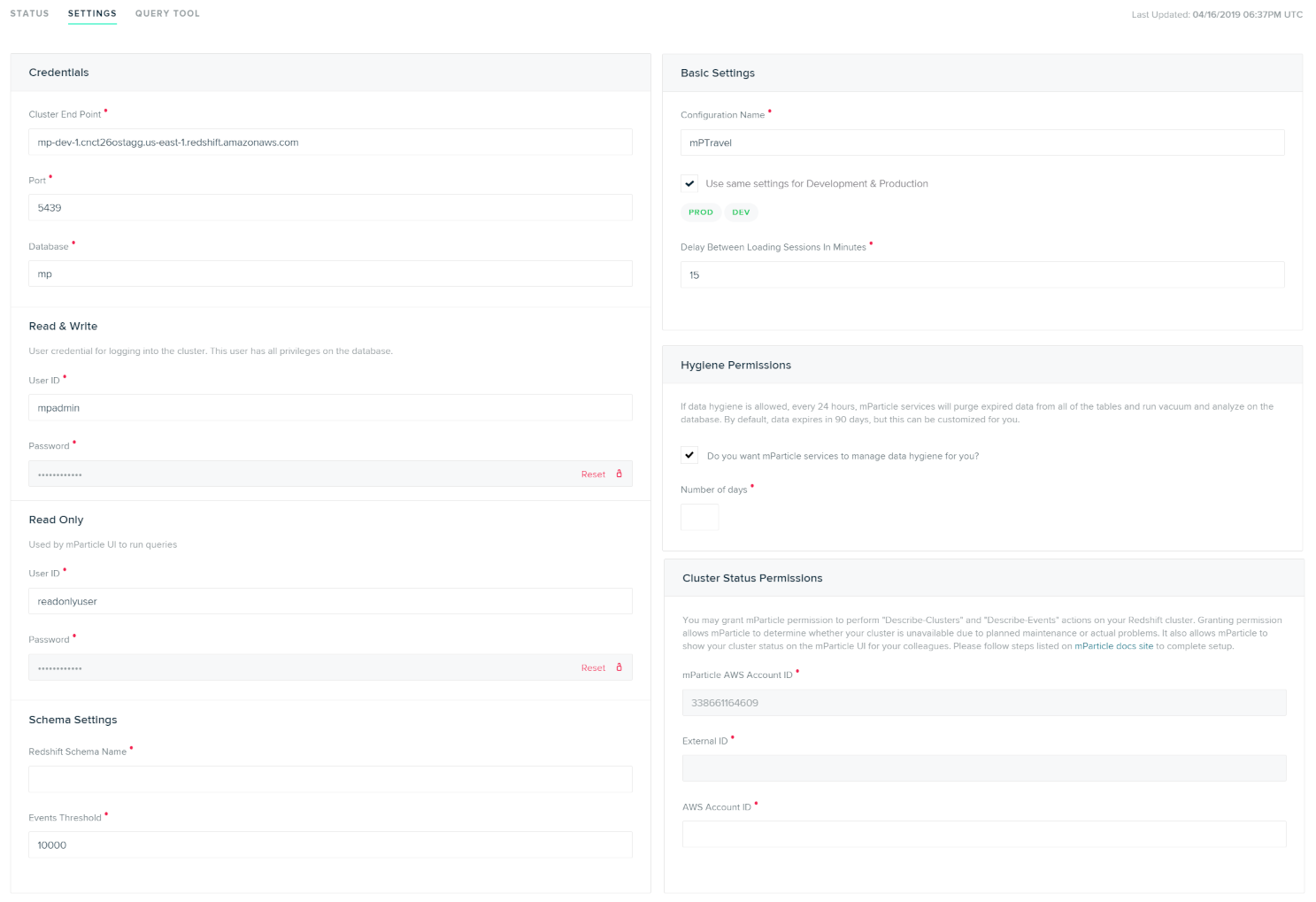
Configuration Settings
| Setting Name | Data Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster Endpoint | string |
Endpoint string shown on Configuration tab on your Redshift Dashboard. | |
| Port | number |
5439 | Open port for your cluster. You can find this on the details page for your cluster in Redshift. |
| Database | string |
The name of the database where you want to store mParticle Data. | |
| Read & Write User ID | string |
User ID for the dataloader user you created in your Redshift setup. These credentials will be used to manage the schema and load data. |
|
| Read & Write Password | string |
The password for the dataloader user. |
|
| Read Only User ID | string |
User ID for the readonlyuser user you created in your Redshift setup. These credentials will be used when running queries from the mParticle UI. |
|
| Read & Write Password | string |
The password for the readonlyuser user. |
|
| Redshift Schema Name | string |
Name of an existing schema where you want to store mParticle data. | |
| Events Threshold | number |
10000 | The number of times a custom or commerce event name must be received in 30 day period for mParticle to create a dedicated table for that event. |
| Delay Between Loading Sessions in Minutes | number |
15 | Allows you to adjust how often you want to load data into the data warehouse. Note that the minimum time is 1 minute and the maximum time is 24 hours (60 minutes x 24). |
| Send user attribute columns | bool |
true |
If enabled, individual columns are created for each user attribute |
| Store device stamp | bool |
false | Store device application stamp in the mParticleDeviceID column. Note that this change does not apply retroactively to tables that have already been created. Data deletion and a replay will be needed in order for existing tables to include this column. |
| Hygiene Permissions | bool |
true | If enabled, every 24 hours, mParticle will purge data over a certain age and perform vacuum and analyze commands on your database. |
| Number of Days | number |
90 | If Data Hygiene is enabled, this is the age in days past which data is purged. |
Once your Data Warehose integration is configured, connect individual inputs to the Amazon Redshift output from the Connections page. You must connect every input you want to store data for.
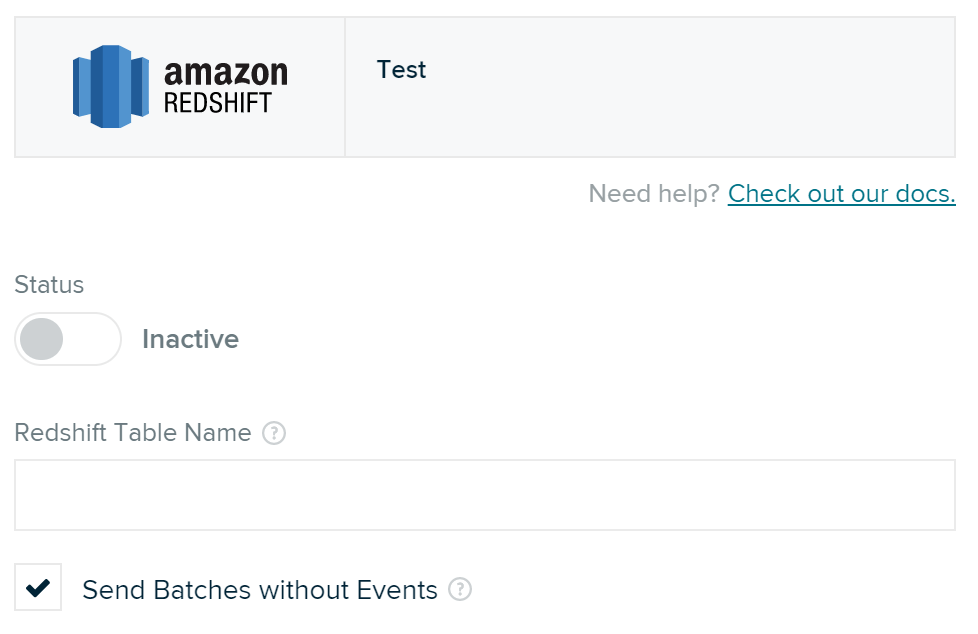
Connection Settings
| Setting Name | Data Type | Default Value | Platform | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redshift Table Name | string |
Feed | Table name for this partner feed. If not set, the partner name will be used. Only applicable to feeds inputs, no effect on apps inputs. If “Split Partner Feed Data by Event Name” checkbox is enabled, this setting is not used. | |
| Split Partner Feed Data by Event Name | boolean |
False | Feed | If enabled, split partner feed data by event name. Otherwise load data into the same table. |
| Send Batches without Events | boolean |
True | All | If enabled, an event batch that contains no events will be forwarded. |
Data Schema
Each common custom event name and eCommerce event name have their own table in Redshift, and all other event names (e.g., session-start, session-end) are stored in a single “otherevents” table. The naming conversion of the table names are as follows.
- A custom event name will have a table named event_[event type]_[event name]. For example, a custom event of event type Navigation named SignUp will have a table named event_navigation_signup.
- An eCommerce event name will have a table named ecomm_[event name].
- Consent events have tables named consent_given and consent_rejected
- All other events are stored in a table named otherevents.
mParticle also creates two views, which can be used to get aggregated views of your app data.
- Under each schema, a view called eventsview that unions all tables under the schema.
- Under the “public” schema, a view called eventsview that unions all eventsview views from all schema in the database.
Common Columns
Each table has the following common columns.
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AppId | int | mParticle app Id |
| AppPlatformId | int | mParticle AppPlatformId, e.g., Google Now app has iOS platform and Android platform, and each platform has an unique mParticle AppPlatformId |
| AppName | varchar(255) | App name |
| AppVersion | varchar(255) | App version |
| PackageName | varchar(255) | App package name |
| AppArchitecture | varchar(255) | App architecture |
| IsPirated | bool | Is the device pirated? |
| ApplicationBuildNumber | varchar(255) | Application build number |
| IsDebugSigning | bool | Is the app debug signing? |
| UpgradeDate | bigint | App upgrade timestamp |
| AppEnvironment | varchar(255) | App environment, debug or production |
| InstallReferrer | varchar(255) | Install referrer |
| Brand | varchar(255) | Device brand |
| Product | varchar(255) | Device product |
| DeviceName | varchar(255) | Device name |
| DeviceUdid | varchar(255) | Device UDID |
| Manufacturer | varchar(255) | Device manufacturer |
| Platform | varchar(255) | Device platform |
| OSVersion | varchar(255) | Device OS version |
| DeviceModel | varchar(255) | Device model |
| LocaleCountry | varchar(255) | Device’s locale country |
| LocaleLanguage | varchar(255) | Device’s locale language |
| NetworkCountry | varchar(255) | Network country |
| NetworkCarrier | varchar(255) | Network carrier name |
| ScreenHeight | int | Device’s screen height |
| ScreenWidth | int | Device’s screen width |
| ScreenDpi | int | Device’s screen dpi |
| DeviceUtcOffset | int | Device UTC offset |
| OsVersionInt | int | Android OS version int |
| Jailbroken | varchar(255) | Device’s jailbroken status |
| IDFA | varchar(255) | iOS IDFA |
| GoogleAID | varchar(255) | Android Google Advertising ID |
| Architecture | varchar(255) | Device architecture |
| IsTablet | bool | Is the device a tablet? |
| VendorIdentifier | varchar(255) | iOS vendor identifier |
| Pushtoken | varchar(255) | Push token |
| AttributionServiceProvider | varchar(255) | Attribution service provider name |
| AttributionPublisher | varchar(255) | Attributed publisher name |
| AttributionCampaign | varchar(255) | Attributed campaign name |
| mParticleUserId | bigint | UserId assigned by mParticle |
| CustomerId | varchar(255) | User’s customerID, usually this is the unique userId in your system |
| FacebookId | varchar(255) | User’s Facebook user Id |
| TwitterId | varchar(255) | User’s Twitter ID |
| GoogleUserId | varchar(255) | User’s Google ID |
| MicrosoftUserId | varchar(255) | User’s Microsoft ID |
| YahooUserId | varchar(255) | User’s Yahoo ID |
| varchar(255) | User’s email | |
| OtherUserId | varchar(255) | “Other” type user identity |
| IsDebug | bool | True for debug environment and false for production environment |
| BatchId | bigint | A unique ID of the batch |
| BatchTimestamp | bigint | Batch timestamp |
| SdkVersion | varchar(255) | mParticle SDK version |
| ClientIp | varchar(20) | Client IP address |
| ClientIpV6 | varchar(45) | Client IP address (compatible with v6) |
| GeoLookupInfo | varchar(1024) | Geo lookup information |
| entrypointtype | smallint | Type of incoming data, Type of incoming data, 1 means from SDK and 128 means from S2S |
| CountryCode | varchar(255) | Country code |
| CityName | varchar(255) | City name |
| PostalCode | varchar(255) | Postal code |
| RegionCode | varchar(255) | Geo region code |
| Latitude | double | Geo latitude |
| Longitude | double | Geo longitude |
| Accuracy | double | Geo accuracy |
| AudienceMembership | varchar(2048) | A array of mParticle segment ID’s the user was a member of at the time of the event |
| SessionId | bigint | A unique ID of the session |
| SessionStartTimestamp | bigint | Session start timestamp |
| EventId | bigint | A unique ID of the event |
| EventTimestamp | bigint | Event timestamp |
| MessageTypeId | int | Message Type Id 1 = Session Start 2 = Session End 3 = Screen View 4 = App Event 5 = Crash Report 6 = Opt Out 7 = First Run 8 = PreAttribution 9 = Push Registration 10 = Application State Transition 11 = Push Message 12 = Network Performance 13 = Breadcrumb 14 = Profile 15 = Push Reaction 16 = Commerce Event 17 = UserAttributeChange 18 = UserIdentityChange 19 = Uninstall |
| EventStartTimestamp | bigint | Event start timestamp |
| EventDate | date | Event date. Sort key |
| EventHour | datetime | Event hour. Sort key |
| EventName | varchar(255) | Event name |
| EventTypeId | int | Event type Id |
| EventLength | bigint | How long did the event take? Represents session length in milliseconds on session end events |
| EventLtvValue | double | Monetary value extracted from the event |
| DataConnectionType | varchar(255) | Data connection type |
| ExceptionHandled | bool | Handled exception or crash |
| IsFirstRunEvent | bool | Is this a first run event? |
| FirstSeenTimestamp | bigint | Timestamp of the first event on this user |
| IsUpgradeEvent | bool | Is this an app upgrade event? |
| SuccessfullyClosed | bool | Is the last session successfully closed? Will be false if app is forcefully killed |
| ApplicationTransitionTypeId | smallint | Application Transition TypeId. AppInit = 1 AppExit = 2 AppBackground = 3 AppForeground = 4 |
| eventcustomflags | varchar(2048) | Event custom flags |
| EventAttributes | varchar(10240) | A JSON string that contains key/value pairs of event attribute names and values |
| UserAttributes | varchar(10240) | A JSON string that contains key/value pairs of user attribute names and values |
eCommerce Only Columns
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ProductActionTypeId | smallint | eCommerce Product Action Type Id 0 = unknown 1 = add_to_cart 2 = remove_from_cart 3 = checkout 4 = checkout_option 5 = click 6 = view_detail 7 = purchase 8 = refund 9 = add_to_wishlist 10 = remove_from_wishlist |
| EcommerceScreenName | varchar(50) | eCommerce screen name |
| EcommerceIsNonInteractive | bool | Is eCommerce action interactive? |
| PromotionActionTypeId | smallint | Promotion Action Type Id 0 = unknown 1 = view 2 = click |
| ProductAction | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing product action details |
| PromotionAction | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing promotion action details |
| ProductImpressions | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing product impressions |
| ShoppingCart | varchar(5000) | JSON string representing shopping cart info |
Event and User Attribute Columns
Each individual event name table (not including otherevents) also has one column per event attribute, named like: “ea[attribute_name]”, and one column per user attribute, named like “ua[attribute_name]“.
The benefit of these individual attribute columns is that you don’t have to use slower JSON parse functions in your query to extract attribute values from either EventAttributes or UserAttributes columns. If you wish, individual User Attribute columns can be turned off by disabling the Send user attribute columns setting.
Partner Feed Data
Events from each connected Partner Feed will be stored under a single table unless the Split Partner Feed Data by Event Name checkbox is enabled. You can choose the table name for each Feed in the Connection Settings.
Device Application Stamp Forwarding
Events can be forwarded with a Device Application Stamp stored in the device ID column. You can enable this in the settings page for your data warehouse configuration by toggling the Store Device Stamp checkbox.
Error Handling
mParticle loads data into Redshift via Amazon S3 and can tolerate the Redshift cluster being unavailable for up to 30 days, depending on data volume. In the event of extended downtime on your cluster, a data replay can be arranged.
- Last Updated: March 13, 2026